It is very difficult to imagine our garden without such delicious and. Even in the smallest area, you can find a garden bed for this wonderful plant, since it does not take up much space. But the benefits of a pea bed will be, and considerable, because in addition to delicious grains, peas have the ability to enrich the soil with nitrogen. And in order for peas to give a good harvest, it is very important to correctly determine when to plant them in the ground.
Planting dates for peas
Since peas are cold-tolerant crops, the dates for sowing come early enough. You can start sowing peas as soon as the soil in the area thaws, and this usually happens by mid-end of April. The main thing is to plant as soon as possible after preparing the soil. You should hurry so that the moisture accumulated in it during the winter does not have time to evaporate from the soil and the peas can germinate safely. If you sow several varieties of peas of different ripeness at the same time, then you can feast on the harvest throughout almost the entire summer.
Peas are herbaceous plants of the legume family. Southwest Asia is home to this culture. Green peas contain carotene, vitamin A, vitamin C, PP, B vitamins, potassium, phosphorus and iron.
Peas are a source of lysine. It is one of the most deficient amino acids in foods. At the moment, 3 types of peas are grown:
- Vegetable.
- Stern.
- Grain.
This legume belongs to self-pollinating annuals. Peas are not only used in cooking. This is one of the best siderates... Almost any vegetable crops can be planted in the soil after peas.
Description
 The plant has a deep root system. The branching stem reaches up to 2 meters in length. Composite leaves have antennae at the end. With these antennae, the leaves entangle the support to support the stems. During the growing season, the plant blooms with purple or white flowers.
The plant has a deep root system. The branching stem reaches up to 2 meters in length. Composite leaves have antennae at the end. With these antennae, the leaves entangle the support to support the stems. During the growing season, the plant blooms with purple or white flowers.
Flowers of early varieties hatch from the bosom of 6-8 leaves. Late varieties dissolve its flowers from the axils of 12-24 leaves. A new peduncle is formed almost every day.
Leguminous fruits, depending on the variety, have a different size, color and shape. Peas have the property of enriching the soil with nitrogen. This property is due to microorganisms that are located on the roots of the culture. These microorganisms extract nitrogen from the air and then enrich the soil with it.
Varieties
Pea varieties are divided according to their intended purpose.
Peeling have smooth seeds. They contain a large amount of starch.

Brain varieties... Fruits shrivel towards ripeness. Beans have a lot of sugar. Brain varieties are good for canning and freezing.
- Alpha is an early crop. The growing season is 55 days. The pods are saber-shaped. Possesses good taste.
- Adagumsky. A variety of medium ripening speed. Seeds are greenish-yellow in color.
- Vera. Early maturity plant. The pods are 6 to 9 centimeters long. One pod contains up to 10 peas.
Sugar... These varieties have small seeds. There is no parchment layer in the pod. The absence of this layer allows peas to be consumed along with the pods.

How to plant peas outdoors
Peas are planted in open ground at the end of April. It is necessary to plant from the twentieth, when the ground dries up from snow. Peas are able to survive light frosts... This property allows you to sow crops at an early date.
Peas are planted several times. The first planting takes place from the end of April, and the second after 10 days. The planting material is heated in boric acid. The boric acid temperature for heating the seeds is 40 degrees. A solution should be prepared from 2 grams of sulfuric acid per 10 liters of water. Warming up takes no more than 5 minutes. This procedure allows you to protect the seed from diseases and pests.
The seeds should dry out after swelling in the solution. If this procedure has not been carried out, then the seeds must be planted dry. The existing seeds will swell in the ground by the evening.
The soil
Choose the right piece of land for planting peas in open ground.
- For peas, you need to choose a well-lit area of land.
- Light soil is preferred for sowing.
- Requires medium acidity of the soil for growing peas. Culture perishes in the acidic earth.
- The plant does not tolerate dining soil. It is advisable to fertilize the soil before planting.
 Peas grow well near the apple tree. The apple tree does not shade the sun for the peas. In turn, the plant enriches the soil with nitrogen to feed the tree.
Peas grow well near the apple tree. The apple tree does not shade the sun for the peas. In turn, the plant enriches the soil with nitrogen to feed the tree.
Planting of the crop begins in early spring when the snow has melted. Soil preparation is carried out in the fall. First, the earth is dug up, and then 20 grams of potassium salt and 50 grams of superphosphate are added to it. Soil acid is neutralized by adding wood ash.
In the spring, before planting, 10 grams of saltpeter is applied per 1 meter of land. Fresh manure must not be used as fertilizer for peas. The culture does not tolerate fresh manure. But it grows well in the soil, which was fertilized with manure in the past.
Landing rules
Planting culture is carried out according to the following scheme:
- The first step is to dig a furrow 5 centimeters deep and 15 wide. The furrow spacing is 50 centimeters.
- Compost with ash is introduced into the furrow. A small amount of garden soil is sprinkled on top of the furrow. The depth of the furrow after top dressing is 3 centimeters.
- 15 seeds are sown per 1 meter of furrow. The distance between the seeds is approximately 5 centimeters.
- Furrows are buried to ground level after planting. After, the earth is compacted and slightly trampled. This measure allows you to protect the seed from birds.
- Furrows are covered with polyethylene until germination appears. The first shoots appear 1-2 weeks after sowing.
Radish or lettuce can be grown between the rows of peas.
Care
 Seeds germinate at a temperature of 4-7 degrees. For a culture, the optimum temperature will be 10 degrees. The plant does not tolerate a hot climate. Plants planted in the heat will not bloom.
Seeds germinate at a temperature of 4-7 degrees. For a culture, the optimum temperature will be 10 degrees. The plant does not tolerate a hot climate. Plants planted in the heat will not bloom.
Basic pea care consists in the timely watering and weeding of the earth. The first loosening is carried out by hilling pea bushes. This happens 2 weeks after germination.
Pinching the top of the stem allows you to harvest a little earlier. The stems begin to move away from the pinching site. These stems can also be pinched. It is necessary to pinch in the morning so that the wound heals by evening.
Watering
Peas do not tolerate heat well. On hot days, it is necessary to ensure timely watering. During the growing season, the culture needs especially careful watering. During the flowering period, the plant is watered 2 times every 1 week. The rest of the time, 1 watering per week is enough... Weeding and loosening should be done after each watering.
Top dressing
For feeding, a solution of nitroammofoska is used. A tablespoon of powder is diluted for 10 liters of water. Fertilization with a mullein diluted in water is also allowed. In the spring, nitrogen-containing fertilizers are applied. Peas take potassium-phosphorus fertilizer well.
Garter
The culture has weak stems. Under the influence of pea pods, the stems bend. To prevent the stems from breaking, they must be tied up. Dug-in pegs or wire arches are suitable for a garter. The pegs are dug in at different ends of the trench. Ropes are pulled between the pegs. The pegs must be stable and the rope strong. Pea stalks are tied to this rope.
Pests
Peas are threatened by the following pests:
- Fruit moth.
- Leaf roll.
- Garden scoop.
Scoops and leafworms lay eggs on crop stems. After hatching, caterpillars begin to eat leaves and peas. Insecticides are used to control insects.
Peas are harmed not only by insects, but also diseases... Powdery mildew and mosaic are some of these diseases. Fungicides are used to combat these diseases.
Harvest
 Harvested one month after flowering. Fruiting of the culture occurs within 40 days. The first to ripen are peas in the lower parts of the shrub. Up to 4 kilograms of the crop can be harvested from one square meter.
Harvested one month after flowering. Fruiting of the culture occurs within 40 days. The first to ripen are peas in the lower parts of the shrub. Up to 4 kilograms of the crop can be harvested from one square meter.
Gardeners recommend growing sugar and shelling plants. These peas have good culinary characteristics. If all the pods are harvested after ripening, then by the end of August the shrub will be harvested again.
Peeling varieties are harvested from the end of June. This crop yields until autumn.... The husk is grown for the green peas. Green peas are stored canned. For storage, boil the peas in boiling water for 2 minutes. Further, it is washed through a sieve and cooled in cold water. After cooling, it is dried at a temperature of 45 degrees. Drying takes about 10 minutes. After 10 minutes, the temperature in the dryer rises to 60 degrees. It is necessary to dry it until wrinkles appear.
Arrangement of a vegetable garden in the country involves the cultivation of numerous vegetables, fresh herbs, berry crops.
Optimal use of its area is a skill that not everyone has. For example, planting peas will not only diversify the assortment, but due to their biological characteristics, peas will not take up much space.
Therefore, you should not deny yourself the opportunity to grow familiar green pods.
Fulfilling all the requirements for agricultural technology, you will get a wonderful vegetable plant, from which you can prepare a lot of tasty and healthy dishes.
Biological features, popular varieties
Peas are from the legume family. It is a herbaceous annual with a hollow stem that branches and clings to vertical supports with tendrils. The height of the plant, depending on the variety, ranges from 15 cm to 2.5 m. The flowers are mainly white or purple, butterflies.
The fruits are of two types:
- shelling type - have inedible valves due to the presence of a hard parchment layer (varieties Early Gribovskiy 11, Kubanets 1126, Early 301. Vegetable 76, Alpha, Excellent 240, Viola, Yubileiny 1512, Late-ripening cerebral, Belladonna 136 and others);
- sugar type - there is no parchment layer, so the whole pod is eaten (varieties Zhegalova 112, Inexhaustible 195).
The first type is suitable for canning, the second is used in the preparation of salads and soups.
This plant is resistant to cold, but the temperature optimum is 16-20 ’C. A distinctive feature of vegetable peas is the ability to assimilate atmospheric nitrogen.
Also, peas are picky about soil moisture and can only withstand short-term drought. Thanks to its developed tap root system, it can extract water from deep soil layers.
Peas contain protein, fiber, sugar, starch. It is also rich in lysine (amino acid), vitamins B, PP, A, ascorbic acid. However, people suffering from flatulence should use this vegetable with extreme caution.
In addition to the utilitarian purpose, peas will become an adornment of your decorative garden, because its green stems with twisting tendrils and beautiful flowers look like a ball of decorative wire, which looks very original.
How to plant peas?
Crop rotation in the garden is a prerequisite for a good harvest for many years. Therefore, peas grow best in the place of cucumbers, cabbage, tomatoes, potatoes, perennial grasses. After 4 years, it can be returned to the chosen location.

The soil should be cultivated, well fertilized, light loamy or sandy loam. On another type of soil, the plant will also grow, but it will be depressed, the harvest will be poor. Acidic soil with a high salt content and high groundwater is unsuitable.
A place for growing peas in the country it is better to choose sunny, open or slightly shaded. Before planting, it is imperative to carry out soil cultivation. The bed is dug up, loosened and leveled.
The plant does not carry a lot of nutrients from the ground, so if the soil is fertile, then fertilization is not worth it. On poor soils, it is necessary to add organic matter (per 1 sq. M. - up to 3 kg of humus or compost), mineral fertilizers (in the fall - phosphorus-potassium, in the spring - nitrogen). To reduce acidity, you can add phosphate rock.

Also, do not underestimate the role of micronutrients, which are also important for peas. These are boron, copper, molybdenum, which are applied right before sowing. They can also be used to process seeds. For all legumes, if desired, fertilizers such as nitragin, azotobacterin and others are also used.
When to plant peas? Sowing dates should be the earliest, but the soil should already thaw. Moreover, it is necessary to sow the seeds no later than 6 hours after the spring preparation of the land.

This is necessary so that moisture, which is needed for germination, does not evaporate from the dug up beds. First, the early varieties are planted, then the middle ones and, finally, the late ones. The pre-treated seeds are planted to a depth of 5 cm at a distance of 2 cm.
Care basics
It is important not only to plant the peas correctly, but also to properly care for them, which consists in watering, weeding, pest and disease control, and loosening. Usually, watering is carried out in a drought. To protect the plants from birds, a net is pulled over the plantings.
In addition to weeding, weeds can be fought with herbicides (tropotox, prometrine). Against fungal diseases, it is necessary to use 1% Bordeaux liquid. From aphids - phosphamide, karbofos.

Also, in order to grow peas, you need to make supports for it.... If it is planted near a fence, then just pull the rope. On the garden bed, you can put wire arcs and pull the fishing line or thin rope. The use of supports will increase the yield.
It takes 12-16 weeks for peas to ripen, depending on the variety. It is harvested by hand in the early morning.
Many summer residents grow peas on their plot. It is a herb belonging to the legume family. Green peas contain carotene, vitamins C, PP, group B, potassium, phosphorus, manganese and iron salts. In addition, it contains lysine, a very rare amino acid. Gardeners grow three varieties of peas: vegetable, grain and fodder, from which you can then prepare various dishes. Let's consider in more detail what peas are, planting and care in the open field.
Description
The stem of the plant is hollow, branching, capable of reaching a height of 2.5 m. The leaves are pinnate, with the petioles ending in tendrils. By clinging to the support, they help keep the plant upright. The root system is deep, the flowers are white or purple, bisexual, self-pollinating, propagated by seeds. They bloom in a month or two after sowing. The fruits are beans that come in a variety of shapes, sizes and colors. This plant enriches the soil with nitrogen, since during its growth beneficial microorganisms develop on its roots, fixing nitrogen absorbed from the atmosphere.
Planting peas in open ground
When to plant peas outdoors?
In different regions of Russia, the timing of sowing such a crop is different and it depends on climatic conditions, peas grow well both in the central part of Russia and in Siberia, in the Urals. You should know that pea seeds are able to germinate at a temperature of + 2 ... +5 degrees and they are not afraid of small frosts (up to -5 degrees).
Agronomists recommend sowing such a crop as early as possible. This allows the peas to be less affected by diseases and pests. When should you do this? As soon as the soil is completely thawed and warmed up to a suitable temperature, then you can start sowing. It is not necessary to wait until it gets completely warmer, since peas are hygrophilous, and after winter, the soil is moist, which is required for good germination.
Can peas be planted in autumn? Many gardeners practice winter sowing... For this, dry seeds are planted in frozen soil when there is no longer any heat. In this case, the seeds should not be processed with anything, so that they do not germinate, otherwise they will die.
 To harvest at different times, peas should be planted in 10 - 12 days. To obtain early peas, seedlings can be grown at home, after which they are planted in the ground. To determine when to plant peas for seedlings, you need to know the characteristics of the variety and the desired harvest time.
To harvest at different times, peas should be planted in 10 - 12 days. To obtain early peas, seedlings can be grown at home, after which they are planted in the ground. To determine when to plant peas for seedlings, you need to know the characteristics of the variety and the desired harvest time.
If you want to get peas already in June, seedlings should be planted in March, and varieties for this are chosen smooth-grain or ultra-early wrinkled. To harvest in August, sowing is carried out in April - May. Summer sowing is completed by mid-July in order to get a harvest in September-October, but on condition that ultra-early ripening varieties are planted.
Seed treatment
Pea fruits can be enjoyed the whole summer, since it can be planted several times. Planting of varieties is carried out in the last days of April, when the sun begins to warm up, and the soil departs after the winter cold. Then it is recommended to sow peas at the end of June. In this case, the fruits fully ripen in mid-August.
Before planting, you need to prepare the seeds. If the seed peas were harvested on their own, then heavy peas should be selected. To do this, the seeds must be soaked in salt water. Usually empty and unusable float up, but full-weight material remains below.
The collected rejected peas must be thrown away, after which the water is drained, and the remaining seeds are dried. So that they sprout quickly they should be soaked a day before planting... To do this, natural fabric is abundantly moistened with clean water, peas are wrapped in it and placed in a plastic bag.
The soil
Where is the best place to plant peas? Growing peas in the open field requires compliance with certain conditions: the site must be sunny, and groundwater - to lie deep, because the roots of a plant are able to go deep into the depth of a meter and water can damage them. The soil in which the crop will be grown should be light but fertile.
Peas do not like poor soil, as well as such soil that is rich in nitrogen. Some gardeners recommend planting the plant in the near-stem circles of young apple trees, since their developing crowns do not block it from the sun, and at the same time, peas begin to enrich the soil with nitrogen necessary for trees. In this case, fertile soil with a height of 10 - 12 cm should be poured into the tree trunks of apple trees.
Although peas begin to grow from seeds in early spring, it is best to prepare the soil for them in the fall. To do this, they dig it up and additionally add 50 g of superphosphate and 20 g of potassium salt to each m2. If the soil is acidic, then it should be neutralized with wood ash. Next spring, 10 g of saltpeter per m2 should be added to the soil. It is forbidden to use fresh manure as fertilizer, because the plant does not like it.
After that, you can sow the seeds. Peas grow well after the following plants:
- pumpkin;
- cucumber;
- cabbage;
- potatoes;
- tomato.
Cultivation of crops is not carried out in the soil in which they grew:
- beans;
- beans;
- peanut;
- lentils;
- directly the peas themselves.
How to plant peas outdoors?
Before sowing, the soil should be leveled and watered. How to plant peas correctly? The crop planting scheme is very simple: in the beds you need to make furrows 15 - 20 cm wide and 5 - 7 cm deep at a distance of 50 - 60 cm from each other. Compost mixed with ash is added to the furrows, and it is sprinkled with garden soil on top. Sowing is carried out in such a way that the distance between the seeds is approximately 6 cm.
The furrows should be covered with earth, then it is compacted so that moisture remains in the soil. To protect the peas from birds, you need to cover the area with a transparent film. The emergence of seedlings is expected in 1 - 1.5 weeks. In the aisles of the peas, lettuce or radish can be grown.
Growing
 Seeds can germinate at 4-7 degrees, but the most comfortable temperature for them is 10 degrees. This plant categorically does not tolerate heat, therefore, seeds planted in hot weather will not give flowers later.
Seeds can germinate at 4-7 degrees, but the most comfortable temperature for them is 10 degrees. This plant categorically does not tolerate heat, therefore, seeds planted in hot weather will not give flowers later.
Crop care implies proper watering and further loosening with simultaneous weeding of the area, otherwise it is not very difficult to care for. The first time the soil needs to be loosened 2 weeks after the shoots appear, while pea bushes should huddle.
As soon as the plant stretches in height by 20 - 25 cm, then along the row it is necessary put supports... Peas will climb up on them.
To grow peas and get a rich harvest, you should as early as possible pinch the top of the stem... In this case, he begins to start up side shoots, which then also need to be pinched. This manipulation is best done in an early sunny morning, so that the wound dries up by evening.
Watering
Such a culture does not tolerate heat, so in dry weather it needs to be watered vigorously. Peas especially need moisture when flowers appear. If before that the plant is usually watered once a week, then during flowering and fruit formation, watering is carried out twice a week. Also, peas need to be watered as often as possible in the heat and quite abundantly. After watering, the site is weeded and loosened.




Top dressing
Watering the crop should be combined with top dressing. Before watering, you need to dissolve a tablespoon of nitroammofoska in 10 liters of water - this is how much solution is required for one square meter of a pea bed. After that, it is recommended to add mullein solution. Before flowering, add:
- potash-phosphorus fertilizers;
- dry organic matter (humus, compost).
And the second time they are brought in after flowering, as well as in the fall, when the soil is cultivated. Nitrogen fertilizers should be applied to the soil in the spring.
 In such a culture, the stems are rather weak and during the formation of fruits, they begin to sag under their weight, so they need to be tied to a support. As it, metal rods or pegs are used, which are stuck along the row at a distance of 1.5 m from each other. A rope or wire is stretched horizontally on them. Shoots with tendrils should be directed along these stretch marks so that the plant is ventilated and warmed up in the sun, and not lying on the ground and rotting from dampness.
In such a culture, the stems are rather weak and during the formation of fruits, they begin to sag under their weight, so they need to be tied to a support. As it, metal rods or pegs are used, which are stuck along the row at a distance of 1.5 m from each other. A rope or wire is stretched horizontally on them. Shoots with tendrils should be directed along these stretch marks so that the plant is ventilated and warmed up in the sun, and not lying on the ground and rotting from dampness.
Diseases and pests
When growing peas, you can expect attacks on it from various pests. Most often these are:
- garden and cabbage scoop;
- leaf roll;
- pea moth.
Scoops and leaf rollers eggs are usually laid on the leaves of the crop. The caterpillars of the scoop, hatched from them, begin to eat up the ground parts of the plant, and the larvae of the leafworm can wrap themselves in them. Moth moths lay eggs on the leaves, fruits and flowers of peas, which the larvae will feed on in a week.
Peas are most often exposed to diseases such as powdery mildew and mosaic... A fungal disease such as powdery mildew manifests itself as a loose whitish bloom, which occurs first in the lower part of the plant, and then spreads throughout the peas. As a result, the fruits begin to crack and die, and the affected shoots and leaves after a while turn black and die.
When it turns out what the culture is sick with, then it needs to be processed. This helps to fight the fungus, but in order to get rid of the virus, the diseased plant is removed and burned, and the soil in which it grew is spilled with a strong solution of potassium permanganate and nothing is grown in this place for a year.
Fight the fungus help:
- Speed;
- Fundazol;
- Topsin;
- Topaz;
- Quadris.
 It is best to process the leaves in the evening, so that the sun's rays cannot burn the ground parts covered with drops.
It is best to process the leaves in the evening, so that the sun's rays cannot burn the ground parts covered with drops.
Infusions of garlic and tomato tops cope with moths, leaf rollers and scoops. To prepare a tomato infusion, it is necessary to insist 3 kg of chopped tomato tops in 10 liters of water for a day. Filter the infusion before processing. To prepare another infusion, 20 g of garlic is chopped, poured in 10 liters of water and insisted for a day, after which it is filtered and applied.
Thus, green peas, the photo of which is presented in the article, is quite simple to grow outdoors. Planting usually begins after the soil in the garden warms up, but not completely. With proper care for it and following all the necessary recommendations, you can get a bountiful harvest.
Vegetable peas belong to the category of plants that do not require much labor when grown in a summer cottage. In order for it to grow on time and give a full harvest of a delicious delicacy that children especially love, it is necessary not only to choose the right variety, but also to plant seeds in the garden as early as possible, as soon as spring garden work begins. This is a culture that will surely thank the gardener with useful vitamin pods.
Site selection, soil preparation and planting beds
Vegetable peas are subdivided into sugar peas and hulled peas. These species differ in whether they use whole pods for food or only ripe peas. Sugar varieties are most often planted at the dacha, but from the point of view of agricultural technology, this is not important, at least, planting of any types of peas is carried out almost the same. Growing this healthy vegetable crop is not a problem even for a novice gardener.
Peas are a cold-resistant plant, and they begin to sow it as soon as the ground thaws a little after winter, so the garden must be prepared in the fall: in the spring at this time, digging up the site is still very difficult. The garden bed may be the smallest size, there may even be several of them, in the most unnecessary areas, but this should be a place well lit by the sun: peas will also grow in partial shade, but the yield will decrease somewhat. It is very good to sow early sugar peas along the paths, where children will be happy to pick them off without trampling the plantings.
It is advisable to make a comfortable approach to the pea bed for the kids.
Since peas are sown very densely, they very soon grow into a kind of "forest", its stems are entwined with grown weeds, and it is not possible to weed them. Therefore, even the most wasteful area must be free from weeds in advance, at least perennial. Peas love soils, medium in composition: loamy and sandy loam. The soil should be moderately fertilized, but peas do not need a lot of nitrogen fertilizers: they provide themselves with this element, extracting it from everywhere and being considered a nitrogen accumulator.
It is best to apply manure (a bucket per 1 m 2) under the predecessor, and in the fall, dig up a bed for peas with the addition of 20–40 g of superphosphate and 10–20 g of any potassium fertilizer. You can replace this mixture with a liter can of wood ash. If you apply manure directly under the planting of peas, then the bushes grow strongly, branch, late harvest, and sometimes get sick. The best in acidity soils are slightly acidic or neutral, in case of excess acidity they are preliminarily limed.
Pea precursors when planting
Peas are not a capricious plant, and you can sow it after almost any vegetables. Any pumpkin crops (cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkins), as well as all types of cabbage and potatoes are considered the best predecessors. Peas themselves, as well as their related beans, are the best precursors for most of the known vegetables.
You should not grow peas in one place for several years in a row: the soil after it should be occupied by other crops for 3-4 years. Peas should not be planted after any kind of beans.
Preparing seeds for planting
Peas are often sown with seeds from their harvest, since by the end of fruiting, interest in them disappears and many unharvested pods remain, which ripen to full condition. This is normal practice in most cases, unless the sown peas were a hybrid (F1): in this case, you may get a completely different crop than expected. Peas are often planted with dry, freshly purchased seeds, but it is best to take a little time to get them ready for sowing.
Rejection of seeds
Even in the purchased pea seeds, which are in beautiful bags, there are a small number of unusable specimens, and in those grown on their site there may be even more of them. Therefore, it is not superfluous to reject the unfit in advance. Self-collected peas should be checked for damage: they are very often visited by a fire-breaker. Such seeds are permeated with holes, inside of which you can find traces of pests, or even small worms.
You can reject such seeds by hand, sorting them out by the piece, but it will be much faster to pour the seeds into salt water (a tablespoon per liter) and wait a couple of minutes. The frail and infested seeds will not drown; they must be collected and discarded. Drowned ones - rinse with water and dry. After that, you can sow them, but it is better to continue the preparation if there is still a little time left before sowing.
Checking seeds for germination
Pea seeds are suitable for sowing for 5-6 years, but only if stored properly, if they are not periodically dampened. Therefore, in doubtful cases, it is advisable to check them for germination, and to do this even in winter, so that in case of failure, you can buy fresh seeds of the desired variety. For peas, germination is considered good if 9 seeds out of 10 are suitable.
Pea seeds usually germinate easily, but sowing with roots is very inconvenient.
It is very simple to check the germination rate: a dozen seeds are soaked for a couple of hours in water, after which they are transferred to a damp cloth. Place this mini-vegetable garden in any container and cover it loosely with a lid. Twice a day, check whether the fabric is still damp, add water if necessary.
Peas peck after a few days, and after a week everything becomes clear: if only one pea has not sprouted - excellent, two or three - tolerable. If you have less than five tails, it is better to buy new seeds. Although, if there are a lot of old ones, you can sow them, only with a margin, twice as thick as usual.
Is it necessary to carry out soaking and germination of seeds
It is not recommended to soak and germinate pea seeds before sowing. This is especially true of the most delicious and popular cereal peas. What is the reason for this? Yes, most vegetables do best when sown with sprouted seeds. But the fact is that peas are sown very early, in cold soil. If it is sown with non-germinated seeds, they will simply wait until the threat of severe frosts is gone: somehow the seeds feel it. But if the soil temperature drops below 4 ° C, the young roots of the sprouted peas die, and after that the seeds rot.
It makes sense to sow soaked peas only if the early planting dates are hopelessly missed, and you want to get a harvest as soon as possible. If the gardener is sure that the cold will not return, and the soil has warmed up enough, then you can put the seeds on a saucer and pour water so that it only covers the peas. The soaking time is about 12 hours, and during this period it is necessary to change the water 4–5 times.
The peas will become saturated with water and swell, but this procedure will shorten the germination time by a maximum of two days, and even then, if the soil is sufficiently moist. You should not germinate seeds in the classical understanding of this word, that is, before the appearance of the tails: it will be much more difficult to sow them, and this will not give a significant gain.
Video: sowing sprouted peas
Seed treatment before sowing
To make the germination of seeds in the garden more friendly, they can be warmed up dry near the battery by placing them next to it in any rag bag for one and a half to two hours. Chemical treatment may be required to prevent diseases from occurring if they ever occur on the site, but ordinary summer residents almost never do this.
In large agricultural enterprises, peas are pretreated, for example, with formalin.
Some gardeners before sowing (not early!) Treat the seeds with various preparations containing biologically active substances. In this way, they try to support plants in difficult climatic conditions or slightly increase yields. Among the most popular drugs are Epin and Humate (drugs with stimulating, adaptogenic and anti-stress effects). Sometimes, when preparing seeds, microfertilizers are used (preparations of zinc, molybdenum, cobalt). If you do such work, you must do it very carefully, not exceeding the dosage prescribed in the instructions for the chemicals.
Planting dates for peas
The ripening time of the first crop varies greatly depending on the variety, but ordinary summer residents almost always sow early-ripening sugar varieties. The first shoulder blades can be torn off approximately 45 days after sowing. Therefore, it is possible to calculate the sowing time and based on these data. But in practice, peas are sown without hesitation, as soon as the soil allows you to outline rows and go deeper into it a few centimeters. In the central region of our country, depending on the weather, this can be done in mid or late April.
To extend the yield of the crop, it is advisable to sow several varieties: the earliest and medium-early. But in any case, this should be done as early as possible: peas sown closer to summer grow and develop worse: they do not like too hot weather. Deadlines are mid-June. All varieties of peas are remarkably cold-hardy. At the same time, smooth-grain germinates at a soil temperature of +1 o C, and cerebral ones require slightly warmer weather. But any temperature is suitable. For the growth of peas, the optimum temperature is from 12 to 22 o C.
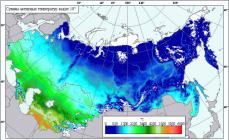
Some gardeners try to focus on the lunar calendar in terms of planting. Although it should be admitted that in recent years, interest in this topic has somewhat subsided, which is due, among other things, to the fact that very different dates of the same garden work are published in various publications. If we analyze various sources, it turns out that in 2018 for sowing peas, the most often favorable dates are 21, 23-28 April, as well as 3-5 May.
Planting dates in different regions
Peas grow well in any climate except very hot ones. If in the central regions of Russia it is sown in April, then in the north - in May, and in the south - already in the first spring month: peas do not like hot weather, and you can get a full harvest only before it arrives. Therefore, for example, in the Krasnodar Territory or the republics of the North Caucasus, it is possible to plant peas already in different dates of March, depending on the current weather.
In the suburbs or in Belarus, where the climate is similar, there are ideal conditions for growing this crop. Sowing dates for peas are very early here, they begin when the soil warms up to 5 ° C, that is, no later than the May Day holidays. Many gardeners sow seeds two to three times, until about June 10. The climate in Ukraine is diverse: it is the second largest country in Europe. If in the north the sowing calendar is similar to the one near Moscow, and peas are sown in mid or late April, then in the southern regions this is done already in the last days of March.
In colder climatic conditions (Siberia, the Urals and the Urals, the North-West region, including the Leningrad region), it is rarely possible to sow peas before the beginning of May, and in some years the land ripens only closer to the middle of the month.
The process of planting peas for seedlings
To get a very early harvest, peas are sometimes grown through seedlings. True, in the apartment a lot of space must be allocated for this, so they try to prepare seedlings in greenhouses or hotbeds. For this purpose, any containers are suitable, in which the seeds are sown every 2-3 cm. The composition of the soil does not matter. For sowing, it is better to use early varieties, such as Early 301 or Viola.
Since there is no need to be afraid of the cold at home, peas are soaked for 10-12 hours before planting, periodically changing the water. Sowing the seeds itself is not difficult: they are buried to a depth of 3-4 cm, having previously marked out frequent grooves, and watered well. Peas emerge in about a week, and seedling care is the most common: keeping the soil moist and monitoring the light and temperature conditions. Peas should be in the sunniest place with a temperature of no higher than 20 o C.
The most difficult thing is picking seedlings, so you can immediately sow it in separate cups, but there will certainly be nowhere to put them in the apartment. In this regard, they often do without picking, but it is not at all easy to unravel the intertwined roots of neighboring plants.
Sometimes seedlings are grown in the so-called hydroponics. To do this, construct a "snail" of toilet paper, which is placed on a plastic wrap, and then the prepared seeds are laid out on the paper, watering abundantly. Having rolled the paper with film into a roll, put it vertically and watered daily.
With this option, the snail should be illuminated for at least 18 hours a day. Two weeks later, the seedlings develop good roots, and after a few more days, the "snail" is unfurled, the peas with roots are carefully separated and transplanted into the garden bed.
Already at the stage of cotyledonous leaves in toilet paper, peas give powerful roots
Transplanting seedlings into the ground
Seedlings in a box with soil are ready for planting in 3-4 weeks, earlier in hydroponics. Carefully removing it from the nursery, it is planted in previously prepared beds. In the middle lane, this is done in the first half of May, in the south - at the end of April.
Seedlings are planted in deep grooves, well watered with water. The landing pattern is 10–12 cm in rows and 35–40 cm between them. If the work is carried out in cloudy weather, the seedlings take root well.
Technology of planting peas with seeds in open ground, step by step instructions
Direct sowing of seeds in the garden at the earliest possible date is the usual method of planting peas. Since the beds are usually ready in autumn, before sowing, grooves are marked at distances of 15-30 cm from one another: less for low-growing varieties, more for two-meter bushes. If the soil has already dried out, the grooves are watered and then peas are sown.
What fertilizers to use when planting
The main doses of fertilizers were applied to the garden bed during the autumn tillage, as mentioned above. In the spring, you just need to loosen the ground with a heavy rake, but before that, you can sprinkle wood ash on the garden bed (about a liter per 1 m 2) and a pinch of urea. Other fertilizers at this moment should not be applied under the peas. If organic matter was not introduced in the fall, then it is not too late to close up good compost in the garden in the spring. Peas respond well to the presence of molybdenum and boron in the soil, but they are rarely applied in the form of purchased fertilizers; the lack of these elements is compensated by the introduction of increased doses of wood ash.
Planting peas as soil fertilizer
Peas are one of the most famous and high quality green manures. This is the name of the plants that are planted not for harvesting, but in order to mow them after regrowth of the green mass and embed them in the soil as fertilizer. Peas are good because they accumulate nitrogen compounds in the soil in a form that is readily available to other plants.
For similar purposes, for example, beans, vetch, oats, lupines, etc. are sown. These are crops, the green mass of which grows very quickly, and then it enriches the soil with valuable nutrients.
When sowing peas for fertilization, the seeds are sown as thickly as possible, after which the crops are systematically watered, and before the peas bloom, they are mowed and all the green mass is dug up along with the soil. The peas have time to go through this entire cycle before planting seedlings of heat-loving crops, such as peppers or tomatoes.
Sowing methods for peas: dry or soaked seeds
As already mentioned, in a very early period, sowing peas with soaked, and even more so with sprouted seeds, is dangerous: in the event of a cold snap, they can disappear. Prepared seeds can be sown not earlier than May, in April it is better to use dry ones. If early ripening varieties are sown along the paths, often even in one row, then peas intended for late consumption are tried to be planted in a more or less large bed: as a rule, mid-ripening, and even more recent varieties grow in the form of very tall bushes that cannot be cultivated without supports.
Based on the estimated height of future plants, and outline the sowing furrows, taking into account the possibility of constructing supports for high-stemmed peas. Peas do not need to be tied up, he himself grasps the obstacles encountered on the path of his growth. And it is better to build them in advance, so that as soon as the first antennae appear, he could already cling to something.
For relatively low bushes, these can be often placed half-meter pegs, but in medium-late varieties, the stems grow up to one and a half meters and more. Therefore, in this case, stakes or rods of the appropriate height or a vertical coarse mesh are required.
The sowing depth depends on the density of the soil and can be from 4 to 10 cm: deeper on sandy soils, shallower on clay soils. Seeds are laid out at a distance of 5–8 cm from one another and buried in the ground, slightly tamping. If it's early spring, don't water. If the soil is already dry, the garden should be watered abundantly, and then mulched with humus or at least dry soil.
Peas are not sown very deeply, but it is necessary that birds do not eat them.
Thus, planting patterns for peas can vary from 5 x 15 cm for the smallest varieties to 10 x 30 cm for the tall ones.
Summer pea care consists of watering and harvesting: loosening and weeding very quickly becomes impossible, and with a good filling of the ridges with fertilizers, you can do without top dressing. Weeds can be cut, but not pulled out, as they are usually abundantly entwined with pea tendrils.
So, the basic steps for planting sugar peas are as follows.
- In the fall, we dig up the site, introducing mineral and organic fertilizers, but not fresh manure.
Digging up a fertilizer bed in the fall is perhaps the most difficult physical job.
- In early spring we prepare seeds: we check for germination, calibrate, but do not soak for early planting.
Soak peas only in case of not very early sowing.
- In the spring we level the garden with a rake, possibly after adding wood ash.
We sow peas depending on the quality of the seeds: if the germination rate was not very good, then it is thicker
- We fill the seeds with soil. If it is dry, water and mulch with humus or dry earth with a layer of up to 1 cm.
We water only if the ground is already dry
Video: sowing peas with dry seeds
Planting peas in the greenhouse
For growing super early harvests, peas are sometimes planted in a greenhouse. Although, of course, a prudent owner would rather spend precious space for growing more thermophilic crops. In unheated greenhouses, including polycarbonate greenhouses, sowing is carried out in March. In greenhouses, only sugar brain varieties are planted, the pods of which you want to eat as early as possible.
Of course, in the greenhouse, it's a pity for a place for peas, but furious amateurs will definitely plant a few bushes
Greenhouse cultivation of peas is no different from ordinary cultivation, except that with the onset of heat, the greenhouse will have to be constantly ventilated: peas do not like heat. In addition, due to high humidity, peas in the greenhouse often get sick with powdery mildew. They plant peas in the same way as they do it in unprotected soil, but do not rely on rain and water more often. To scare off pests, mustard is sown nearby or pre-grown basil seedlings are planted.
Pea compatibility with other plants
Peas enrich the soil with nitrogen compounds, which is undoubtedly useful for its various neighbors in the beds. He is considered a good roommate for most cultures. Many gardeners plant peas even between other plants, several copies each, not for the harvest, but to help them. But do all the neighbors thank the peas for this? Almost everything, it is undesirable to plant it only next to onions or garlic, as well as with the closest relatives - beans and vegetable beans.
The best neighbors of peas are carrots and cucumbers. In addition, you should try to plant spicy herbs or tomatoes nearby, which scare away many harmful insects with their smell. The pea moth is also driven away by mustard. Sometimes peas are sown next to corn, whose tall stalks act as strong supports. Peas live well in the community of cabbage, potatoes, any green crops (parsley, salads, dill).
Peas are a very cold-resistant plant, which is one of the first to be sown. There are almost no failures in obtaining its harvest even among novice gardeners, but it must be planted correctly and on time. Planting too early is impossible: the summer resident simply does not loosen the soil, and if planting too late, it rises more difficult and gives a later and meager harvest.