The study of the properties of functions and their graphs takes a significant place both in school mathematics and in subsequent courses. Moreover, not only in the courses of mathematical and functional analysis, and even not only in other sections of higher mathematics, but also in most narrowly professional subjects. For example, in economics - functions of utility, costs, demand, supply and consumption functions ..., in radio engineering - control functions and response functions, in statistics - distribution functions ... functions. To do this, after studying the following table, I recommend following the link "Function graph transformations".
| Function name | Function formula | Function graph | Chart name | A comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
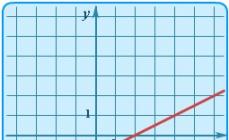
| Linear | y = kx | Straight | The simplest particular case of linear dependence is direct proportionality y = kx, where k≠ 0 - proportionality coefficient. The figure shows an example for k= 1, i.e. in fact, the given graph illustrates the functional dependence, which sets the equality of the value of the function to the value of the argument. | |
| Linear | y = kx + b |  |
Straight | General case of linear dependence: coefficients k and b- any real numbers. Here k = 0.5, b = -1. |
| Quadratic | y = x 2 |  |
Parabola | The simplest case of a quadratic dependence is a symmetric parabola with apex at the origin. |
| Quadratic | y = ax 2 + bx + c |  |
Parabola | General case of quadratic dependence: coefficient a- an arbitrary real number not equal to zero ( a belongs to R, a ≠ 0), b, c- any real numbers. |
| Power | y = x 3 |  |
Cubic parabola | The simplest case is for an odd integer degree. Cases with coefficients are studied in the section "Movement of function graphs". |
| Power | y = x 1/2 |  |
Function graph y = √x |
The simplest case for a fractional power ( x 1/2 = √x). Cases with coefficients are studied in the "Movement of function graphs" section. |
| Power | y = k / x |  |
Hyperbola | The simplest case for a negative integer power ( 1 / x = x-1) - inversely proportional relationship. Here k = 1. |
| Indicative | y = e x |  |
Exhibitor | The exponential dependence is called the exponential function for the base e- an irrational number approximately equal to 2.7182818284590 ... |
| Indicative | y = a x |  |
Exponential function graph | a> 0 and a a... Here's an example for y = 2 x (a = 2 > 1). |
| Indicative | y = a x |  |
Exponential function graph | The exponential function is defined for a> 0 and a≠ 1. The graphs of the function essentially depend on the value of the parameter a... Here's an example for y = 0.5 x (a = 1/2 < 1). |
| Logarithmic | y= ln x |  |
Graph of the logarithmic function for the base e(natural logarithm) is sometimes called logarithm. | |
| Logarithmic | y= log a x |  |
Logarithmic function graph | Logarithms are defined for a> 0 and a≠ 1. The graphs of the function essentially depend on the value of the parameter a... Here's an example for y= log 2 x (a = 2 > 1). |
| Logarithmic | y = log a x |  |
Logarithmic function graph | Logarithms are defined for a> 0 and a≠ 1. The graphs of the function essentially depend on the value of the parameter a... Here's an example for y= log 0.5 x (a = 1/2 < 1). |
| Sinus | y= sin x |  |
Sinusoid | Sine trigonometric function. Cases with coefficients are studied in the "Movement of function graphs" section. |
| Cosine | y= cos x |  |
Cosine | Trigonometric cosine function. Cases with coefficients are studied in the section "Movement of function graphs". |
| Tangent | y= tg x |  |
Tangentoid | Trigonometric tangent function. Cases with coefficients are studied in the "Movement of function graphs" section. |
| Cotangent | y= ctg x |  |
Cotangensoid | Trigonometric cotangent function. Cases with coefficients are studied in the "Movement of function graphs" section. |
| Function name | Function formula | Function graph | Chart name |
|---|
Grade 10
POWER FUNCTION
Exponential calledfunction given by formulawhere, p – some real number.
I ... Indexis an even natural number. Then the power function wheren
D ( y )= (−; +).
2) The range of values of a function is a set of non-negative numbers if:
set of non-positive numbers if:
3) ) . Hence, the functionOy .
4) If, then the function decreases asNS (-; 0] and increases atNS and decreases atNS and increases in the interval)