Densitometry is an effective way to study the mineral structure of bone tissue, allowing to see a picture of a decrease in the density of bones and identify disorders in its structure. This diagnostic technique is used in osteoporosis and other diseases that cause a decrease in the density of bone tissue. The short procedure is absolutely painless, and will not require special training. As a rule, densitometry is carried out on the lumbar spine, on the hip bones, less often - on the forearm, in some cases the entire skeleton may be conducted.
To date, the usual radiographic study is somewhat outdated, it allows you to diagnose only at 25% of the loss of bone mass. Densitometry of the spine allows you to identify the structural change in bone tissue in the range from 1% to 5% of the total bone mass, which makes it possible to diagnose osteoporosis at the earliest stage. Such diagnosis will allow you to appoint timely treatment and reduce the risk of further development of the disease.
Types of densitometry
- X-ray densitometry (two-energy X-ray absorption). This research method provides the most accurate information about the density of bone tissue. The procedure is based on the use of two different X-rays. Dense bone tissue passes fewer rays. Thus, comparing the results of the absorption of the rays, you can identify deviations in the density of bone tissue. The procedure is carried out quickly quickly, and the dose of irradiation does not carry danger to the patient's health.
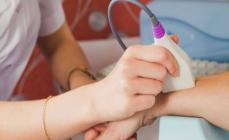
- Ultrasonic densitometry. The procedure is based on obtaining data on the speed of movement of ultrasonic waves according to the bone layers, as well as at fixing the scattering of the waves in the bone cavities. The technique is absolutely safe and does not occupy a large amount of time, but has a lower measurement accuracy, rather than a radiological method.
- Quantitative. The procedure allows to obtain a three-dimensional image of the structural density of bones, but since the method highly loads the body with radiation load, it is very rarely used.
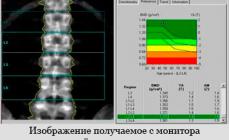
 Nowadays, to diagnose the early stage of osteoporosis, it has become more commonly used ultrasound research methods. This method of diagnosis is an absolutely harmless method, which makes it possible to undergo a survey to children and women during pregnancy. The method allows you to check the various areas of the skeleton with high accuracy. The results of the study are compared with the corresponding norms of indicators, while many patient features are taken into account. The data of the study is displayed on the screen of a densitometer in the form of graphic dependence. The chart is simple enough and does not require special data decryption. The patient immediately receives all the information about the examination, it is diagnosed and prescribed appropriate treatment.
Nowadays, to diagnose the early stage of osteoporosis, it has become more commonly used ultrasound research methods. This method of diagnosis is an absolutely harmless method, which makes it possible to undergo a survey to children and women during pregnancy. The method allows you to check the various areas of the skeleton with high accuracy. The results of the study are compared with the corresponding norms of indicators, while many patient features are taken into account. The data of the study is displayed on the screen of a densitometer in the form of graphic dependence. The chart is simple enough and does not require special data decryption. The patient immediately receives all the information about the examination, it is diagnosed and prescribed appropriate treatment.
In a situation where ultrasound examination establishes significant rates of bone mass, doctors resort to clarifying diagnostics. To do this, the patient needs to undergo a radiographic densitometry. Radiation irradiation on modern densitometers is very small, and does not harm the health of the patient. This technique will allow not only to establish the exact value of the mineral density of bone tissue, but also to know its strength, elasticity, as well as the thickness of the cortical layer and microstructures.
Passage of diagnosis
Preparation for the procedure
Strict instructions for preparation for densitometry do not exist, but still there are certain points that require attention:
- When using drugs containing calcium, it is necessary to abandon them 24 hours before the diagnosis.
- If you have pacemakers or metal implants, you should inform the doctor in advance.
How is diagnostics?
 You will be asked to lie on the horizontal couch, over which the sensor is located reading information about the degree of absorption of X-rays. The emitter itself is under the couch. In the case of a spinal study, you will be asked to bend legs in hip joints and knees, then put them on the stand. During the diagnostics, the body in a fixed position should be fixed.
You will be asked to lie on the horizontal couch, over which the sensor is located reading information about the degree of absorption of X-rays. The emitter itself is under the couch. In the case of a spinal study, you will be asked to bend legs in hip joints and knees, then put them on the stand. During the diagnostics, the body in a fixed position should be fixed.
Contraindications for radiological densitometry
- Pregnancy or period of breast feeding of a child.
- In the case of CT or with the introduction of a contrast agent for 5 last days.
- When passing radioisotope diagnostics within the last 2 days.
Who needs to be surveyed?
- People predisposed to the development of osteoporosis.
- Women over 45 years old and men over 60 years old.
- Persons over 40 years old who had fractures of various kinds.
- Women who took a long time hormonal drugs.
- People accepting drugs contributing to the washing of calcium from the bones.
- People with endocrine or rheumatic diseases.
- Men and women with insufficient body weight.
- People with osteoporosis identified in the usual x-ray examination.
- People who have various diseases of the spine (, kyphosis,).
- Patients suffering from osteoporosis to appoint effective treatment.
Price on the Densitometry of the Spine
The cost of the densitometry of the spine depends largely on the equipment at which the study is carried out, the method of diagnostics, as well as the authority of the clinic. An examination of one spine will cost approximately 1000-2500 rubles, in most cases a lumbar densitometry is carried out. In the case when the study of the entire skeleton is required, the price may amount to 4000-6000 rubles.
Deciphering the results of densitometry
 In the densitometric apparatus, the denominations of the bone tissue density of the human skeleton are laid, various for each individual plot. Based on these norms, age, gender and individual characteristics of the patient, the analysis of bone indicators is analyzed. The main indicators use:
In the densitometric apparatus, the denominations of the bone tissue density of the human skeleton are laid, various for each individual plot. Based on these norms, age, gender and individual characteristics of the patient, the analysis of bone indicators is analyzed. The main indicators use:
- BMC (D) is an indicator of mineral bone content.
- BMD (g / cm2) - indicator of mineral bone density.
The results of the study are presented in the form of two main criteria:
- T-criterion - shows the ratio of the bone density in your body to the density of bone tissue completely healthy person of the same sex and age.
- Z-criterion - shows the ratio of bone density in your body to the average bone density indicator of a group of similar sex people and age.
The norm for the T-criterion is the value from "+2" to "-0.9", when the initial stage of osteopying (reducing the density of bone tissue), the numeric data will be located from "-1" to "-2.5". The development of osteoporosis is characterized by the value below "-2.5". In the case of too low z-criteria values, additional research is most often assigned.
Currently, most modern medical centers provide the possibility of conducting a densitometric survey of the spine. Assign the procedure and determine the frequency of its passage should your attending physician.
This manipulation is currently the most informative means of detection of osteoporosis in its early stages. Densitometry is considered a safe procedure: there are practically no contraindications to its conduct, and there are no side effects and complications after its completion.
The most important sections of the skeleton are subject to the survey, due to which you can predict the development of negative states in the future: femur, forearm and vertebral pole.
Types of densitometry - What is the survey of bone density?
The diagnostic method under consideration is a few species:
- X-ray. Two types of X-rays are used to study the structure of bone tissue. Due to the comparison of the absorption information of the emitted energy, the doctor estimates the level of deviation from the bone density rate. This manipulation takes a minimum of time, and the dose of irradiation is 400 times less than at standard radiography. This type of densitometry appeals when it is necessary to study the bone tasing of the hip joint, shoulder, forearm, lumbosacral spine area, or the entire spinal column.
- Ultrasonic.Due to the lack of any radial load, this technique is considered absolutely safe. It can be used for children, as well as pregnant women. However, the effectiveness of this manipulation is lower than that of X-ray densitometry. Its principle is based on the rate of speed, with which ultrasound-waves apply to bone structures. The bone density is directly proportional to the speed of absorption rays with bone tissue. With significant loss of bone mass, X-ray densitometry is prescribed. It is possible to obtain information about the elasticity, the strength of the cortical layer, as well as the thickness of individual microstructures.
- Quantitative computed tomography . It makes it possible to obtain a three-dimensional picture of the structural density of bone elements. Since the radiation load under this method is very significant, it is used very rarely in practice.
Due to the decrease in the level of calcium in the bones, the diagnostic method under consideration is prescribed to people after reaching the 50 years of age. It is at this age that there is a high probability of appearance Osteoporosiswhich, according to statistics, occupies the third mortality rate.
Measure the value of the mineral density of bone structures is needed by the next category of people:
1. Those who have two or more phenomena provoking:
- Women who have climax at an early age (up to 45 years).
- Brightly pronounced thin.
- The presence of osteoporosis for the nearest relatives.
- Calcium and / or vitamin D deficiency in the daily diet.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Tobacco
- Failures in hormonal background.
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages.
- Corticosteroid treatment.
2. Sugar diabetes.
3. Serious failures in the work of the kidneys.
4. The presence in the history of rheumatic pathologies: systemic red lupus, vasculitis, sclerodermia, etc.
5. Frequent, which may occur even with insignificant injury.
6. A variety of spinal pathologies.
The diagnostic procedure under consideration is not carried out in the following cases:
- The period of tooling the child (for radiological densitometry).
- Deformation in the lumbosacral section of the spine, which impede the patient in the adoption of the right position of the body during the survey.
- Conducting diagnostics using barium contrast less than a week before the indicated manipulation.
Preparation for the bone density survey and stages of densitometry
The type of examination does not require specific training.
However, patients who are appointed densitometry should be remembered for several nuances:
- Preparations containing calcium can distort the results of the diagnosis, so per day before the densitometry, they should be completely abandoned.
- The existence of a pacemaker or a doctor's metal implant needs to be aware of in advance.
- The doctor must be informed about the recently the following manipulations:
- Computer tomography.
- X-ray examination.
- diagnostic measures using contrast substances.
In suspected pregnancy, it is necessary to pre-give the blood test on the HCG. With a positive result, you must put a doctor in fame.
In front of the patient's densitometre asked to remove all metal items: chains, rings, glasses, etc. Their presence can distort the results of diagnostics.

For surveys, two types of systems can be applied:
Stationary
The patient in this case falls on a special table with straightened legs. To study the state of the bottom zone of the spine, the patient is installed under the feet in such a way that the caches are located parallel to the couch.
The radiation source passes over the patient. X-rays fall on the detector, measuring the absorption of rays with bone tissue. The data obtained fall into the computer are processed, and the results of densitometry appear on the monitor.
The patient should not move at this time. In some cases, the doctor may ask for a few seconds to delay their breath.
This procedure, on average, takes 10-20 minutes.
When conducting a standard examination, the X-ray student studies the structure of the femoral bone, the lumbosacral spine zone, as well as the radial bone.
Monoblock
Those parts of the body to be examined (fingers, feet, hands, forearm) are placed in a special niche.
For three minutes you can get the result.
For ultrasonic densitometry You can examine only small areas of the bone: phalanges of the fingers, heels, wrists, etc.
The doctor has a special gel that provides a special slide of the ultrasonic sensor.
The results of the survey are displayed on the monitor.
Results of the diagnosis of the mineral density of the bone tissue of the spine, hips, etc. - what's next?
The decoding of the results is carried out by a radiologist. With the resulting conclusion, the patient needs to go to the rheumatologist or an orthopedic.
In this conclusion, two indicators will appear:
1.T-point
Denotes the mineral density of the patient's bone tissue, in comparison with the tissue density standard of young people.
This indicator is also used to estimate the risk of bone fracture.
The value of T-scales means the following states:
- If the conclusion form indicates a digit in the interval between "+2" and "-0.9", this indicates the absence of degenerative processes in the expired area.
- When varying the results of the study ranging from "-1" to "-2.5", the doctor diagnoses osteopy.
- The value of the specified indicator below "-2.5" is the consequence of the progression of osteoporosis with a high probability of obtaining fractures at the slightest injuries.
2. Z-score
The result obtained in the course is compared with an average of bone density among people identical with a patient of age group, gender and race. The result of the calculations produced and is the specified Z-point.
The decrease in this criterion indicates a reduced mineral density of the patient's bone structures.
No need for a medical diploma to understand the simple truth: calcium is necessary for a healthy skeleton. But even with proper nutrition, the absorption rate and absorption of this valuable element falls noticeably. Densitometry helps to warn heavy consequences for the body. How it is done, how much she is - all this has to learn together with the receipt of the first pension.
Densitometry: What is this procedure?
With age, the likelihood of pathologies associated with the musculoskeletal system increases with age. To prevent the ailments and detects, they use the modern method of instrumental survey - densitometry. Its essence is to determine the content of calcium in bone tissue.
Modern medical centers offer a procedure based on one of the following technologies:
- Ultrasound procedure;
- With x rays;
- Magnetic resonance tomography;
- Methods using computers.
Especially close attention is paid to vertebrae and hip bones: in injuries of these departments, the likelihood of disability is high.
According to the results of irradiation, the device displays a couple of indicators:
- T-points - tissue density at the place of passage of the rays in comparison with normal values \u200b\u200bfor a healthy person;
- Z-score is the same indicator, but in comparison with the average data for a specific age group.

In what cases are prescribed?
Problems with skeleton can escape any person. However, usually the physician prescribes the procedure only if there is sweeping:
- Senior age group: women after 45, men after 60 years;
- Osteoporosis was observed in close relatives;
- Sudden violation of menstruation mode;
- Large mothers after childbirth;
- Survived extensive fractures;
- Extinction of the function of the sexual system (if there is a previous biological time);
- Diabetes;
- Reception of hormonal pharmaceuticals;
- Severe physical work or professional sports;
- Weak motor activity;
- Anorexia and exhaustion of the body with detrimental diets;
- Abundant alphasis of alcohol for a long time;
- Passage of a course of a number of drugs negatively affecting calcium (corticosterone, cortisol, cortisone, diuretic, etc.)
Pictures are issued to the patient in hand. The conclusion of the presence or absence of pathology takes a rheumatologist.

Cost of medical services
It is possible to pass densitometry for free only in some polyclinics with appropriate ultrasound equipment.
To pass the X-ray, computer procedure or MRI, you will need to lay out a rather significant amount of money:
- In the "Invitro" network, where American equipment from "General Electric" is installed, the inspection will cost 1500-2000 rubles;
- "Family Doctor" offers services for approximately the same money - about 1,800 rubles;
- In the "open clinic" prices begin with a level of 1500 rubles.
This price list concerns only Moscow. In regional centers, the service can do significantly cheaper. So, the Voronezh Regional Clinical Advisory Diagnostic Center offers x-ray tissue for 700 rubles.
Before visiting the Medical Center, it is necessary to inquire about the average cost of the service in a particular city. It is necessary to fear both too overpriced and low price tag. Low cost may mean the appropriate quality of service.

Computer Densitometry Bones: What is it?
Computed tomography of bones differs from its analogues in that all images are processed on a special computer. Features of the procedure do not end:
- Snapshots glued in such a way that it turns out the 3D picture, which provides high visuality and facilitates the diagnosis of the doctor;
- In general, a number of cases of computer-based tomography turns out to be the only way to obtain information about tissues;
- The method is used mainly for the study of the state of the spine, but highly efficient when studying the state of any skeleton department;
- One of the few drawbacks is a high proportion of radioactive irradiation. For this reason, the procedure can be contraindicated by some group of people;
- The procedure is rarely prescribed to older people in view of accumulation with age in the bone bone of the adipose tissue, which greatly distorts the test results. Error can reach 15%;
- Patients may not arrange the duration of the session (before half an hour) and the high cost in comparison with MRI and X-ray.

List of contraindications
The dose of irradiation, obtained during the conduct of densitometore, serves as a limiting factor for some groups of the population. The provision of this medical service is prohibited by persons with such pathologies:
- Accumulation of gases in the pleural cavity;
- Open bleeding. Irradiation negatively affects the cells of the red bone marrow, which is due to the failure of hematopoietic processes in the body;
- Increased sensitivity to the radiation source (iodine-125);
- Thyroid diseases;
- Chronic liver diseases or kidney;
- Launched sugar diabetes;
- Spinal pathology that do not allow you to take a stay on the device;
- Lens diseases (for large radiation doses there is a probability of cataracts);
- Patients in serious condition;
- Pregnant women (due to unpredictable radiation action for the future child). If you need to conduct a densitometer, you need to choose in favor of research without ionizing radiation (for example, MRI).
A person undresses, falls on a large smooth surface, and a special scanner passes above it. This is what absolutely painless procedure of densitometry looks like. How it is held and how much it costs in the nearest medical center. With modern equipment there are not only famous clinics of the capital, but also modest regional polyclinics.
Osteoporosis is a disease that wears a progressive systemic nature and is accompanied by a decrease in density indicators with a further change in the structure of bone tissue.
Currently, the issue of the diagnosis of osteoporosis remains fully studied, so the definition of this ailment does not represent any difficulties.

To diagnose patient osteoporosis, comprehensively examine
As a rule, high-quality modern diagnosis of osteoporosis has a complex nature and is based on the evaluation of patient complaints, inspection data, as well as the results of laboratory and instrumental research. On the most informative and common techniques, how to identify osteoporosis, and will be discussed in this article.
Before checking the condition of bones on osteoporosis using laboratory and instrumental methods, it is necessary to determine the factors that could affect the development of the pathological condition of bone tissue.
Make it allows you to carefully collect anamnestic data, examination of the patient and studying its outpatient card.
The most typical factors for the development of osteoporosis are today:
- problems of the gastrointestinal tract, which is accompanied by an impaired calcium suction;
- vitamin D;
- endocrine diseases;
- low body mass coefficient;
- obesity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- early Climax;
- the presence of spinal deformations and other bone elements;
- insufficient number of calcium-containing products in the food diet;
What should be powered by osteoporosis
- prolonged steroids;
- long recovery period after bone injury.
To learn more about various risk factors for the development of osteoporosis, as well as on its main manifestations and stages, special materials will help, for example, Questionnaire "Osteoporosis in women", "osteoporosis and quality of life", "osteoporosis and pain syndrome".
Early diagnosis of osteoporosis is one of the ways of preventing the development of the disease. About other preventive measures read
Methods of diagnostics osteoporosis
If a person has several risk factors for the development of osteoporosis and burded the bones of the history of the history, the doctor will necessarily offer such a patient to undergo a survey on the definition of bone mineral density, the name of which is densitometry. Analysis on osteoporosis of densitometry, the price of which is completely dependent on the method of its implementation, is an assessment of bone density, that is, the coefficient of their saturation of calcium.
Currently, the most informative methods of diagnosis of osteoporosis is considered:
- ultrasonic computer densitometry;
- x-ray densitometry;
- biochemical blood test for osteoporosis.
More about the method of densitometry you will learn from the video:
Ultrasonic computer densitometry
This is the most common method for diagnosing osteoporosis. The essence of the technique is based on the determination of the speed of passage of ultrasound through the tissue with different density indicators: a high density tissue is much faster than ultrasonic waves, rather than dense structures.
The slower passes ultrasound through the bone, the lower its mineral density, and, consequently, above the degree of osteoporosis.
Ultrasonic survey on osteoporosis is carried out using a special extensive equipment. The doctor, watering the sensor in the projection places of the bones affected by the pathological process, has the ability to display the data obtained to the monitor, as well as write them to digital media in order to study these results in the dynamics. The method of ultrasound densitometry is very sensitive, which allows him to respond with maximum accuracy to the slightest changes in the density of bone tissue.
Such qualities make this method of study effective for the diagnosis of initial forms of the pathological process in the bones, when the loss of mineral density does not exceed 4% of the total.

Ultrasonic computer densitometry - the most common method for diagnosing osteoporosis
The most significant advantages of ultrasound densitometry include:
- the absolute harmlessness of the method, when the analysis of osteoporosis - densitometry with ultrasound waves does not carry any threat to the health and normal life of the human body;
- high research informativeness;
- availability and relatively low cost of the methodology;
- quickness of obtaining results: Ultrasound densitometry Osteoporosis indicators allows you to determine within a few minutes from the start of the study;
- no contraindications to the procedure;
- painless method.
Ultrasonic densitometry does not have contraindications, therefore, it is a universal method of determining the density of bone tissue, which can be used even with respect to people with severe pathologies, pregnant women and children.
Absolute testimony to the study of bones with ultrasound are:
- age (for women it is 40 years old, and for men - 60);
- the first signs of osteoporosis in women, which has become breastfed many times or more than more than a year;
- early or pathological climax;
- frequent fractures;
- violation of the function of the parachitoid glands;
- reception of drugs that wash out calcium bones.
X-ray densitometry
X-ray densitometry is quite accurate, but, unfortunately, not the safest method of determining the bone density.
X-ray during osteoporosis allows you to examine on this disease such a skeleton departments such as a loin, a neck of the hip, a loyal area, a ray-tunny joint and the like.
The study is a very efficient and accurate method, but has a number of contraindications due to its ability to irradiate fabrics.
That is why the diagnosis of osteoporosis in women in an interesting position, children, seriously ill is impossible.
X-ray densitometry, being one of the first methods of studying the health of bone tissue, in our time continues to be improved and developed. Such a tendency to limit the destructive influence on the human body makes it possible to recommend this procedure to an increasing number of patients. To see osteoporosis on the X-ray picture, the doctor allows the unique ability of X-rays to weaken when passing through bone structures, which makes it possible to assess the specialist of their surface mineral density.

X-ray densitometry is a very accurate method for the diagnosis of osteoporosis
X-ray signs of osteoporosis - a reduced amount of mineral substances relative to the total area of \u200b\u200bbone tissue, which the X-ray beam passed. Accuracy and accessibility, and the main high informativeness of this procedure made it an excellent alternative to more expensive ultrasound densitometry.
Both methods have both their positive and, naturally, the negative sides.
Therefore, the question of the feasibility of using one or another version of the diagnosis of osteoporosis in the patient should be solved by an exclusively attending physician.
This method is to determine the metabolic indicators in the bones, as the best option of the patient's additional examination.
Diagnose osteoporosis can not only according to the results of instrumental research. The laboratory diagnosis of osteoporosis will also assume the development of this disease, which is based on the quantitative determination of the hormone levels of the internal secretion glands (thyroid, parachite, genital) in human blood, as well as concentration of trace elements, which are responsible for building bone tissue (calcium, magnesium, phosphorus) , in the morning urine of the patient. These and other indicators in medical practice are called osteoporosis markers And are weighty factors capable of confirming the presence of a pathological process and determine the nature of its origin.

Laboratory diagnostics of osteoporosis will help the doctor diagnose osteoporosis
What tests should be passed during osteoporosis solves the attending physician, relying on the results of densitometric studies, history of the patient, its complaints and the presence of clinical manifestations of the ailment.
Biochemical diagnosis allows not only to determine the disease in the early stages of its development, but also is a very informative method of controlling the effectiveness of the treatment carried out, which has already been an estimate of its effectiveness or inexpediency.
When examining a patient with osteoporosis, the following laboratory studies are carried out in obligatory:
- determining the level of hormones of the thyroid gland (TSH, T4);
- blood test for sex hormones (for men - testosterone, for women - estrogens);
- quantitative study on ionizing calcium;
- definition of parathgamon titers;
- control of the level of active vitamin D (25-hydroxyvitamin D).
Other types and methods for determining osteoporosis
Method that allows you to determine the foci of osteoporosis, which remain unnoticed even with x-ray and tomography, is scintigraphy. It is based on the use of contrast phosphate technetium. The ability of a contrast agent to penetrate the bone tissue depends on the quality of metabolism and blood flow in the affected area.
For details on the method, see the video:
Zones with high blood supply and metabolism, which happen during fractures, metastasis, infectious processes, hyperparathyroidism, look at the scintiogram as "hot foci".
In some cases, survey results need differential diagnostics, for example, to determine the true nature of the pathological process: the presence of hidden fractures, osteoporosis or metastases.
More about what scintigraphy, osteoporosis or metastases are visualized on the scintigram and which there are alternatives to this study, the patient will better explain his attending physician.
MRI study It is a high-tech, innovative and sussuctive method for diagnosing the state of internal organs and organism systems, including the determination of bone density. The results of such a survey make it possible to assess the morphological changes in the tissues and trace their functionality. MRI allows you to obtain a contrast image of internal organs in any plane without ionizing irradiation and the introduction of chemicals. To determine the mineral density of bones, MRI is extremely rare. This is due to the high cost of the method and his tendency to hyperdiagnosis.

To diagnose osteoporosis, MRI is used extremely rare
Estimate the possible risks of development of osteoporosis of bones will help genetic research. A comprehensive genetic study allows you to determine disorders in genes, which is responsible for the synthesis of vitamin D, collagen, the functionality of receptors to pararathgormon and much more. Naturally, even if the method shows a high tendency of a person to develop osteoporosis, it is not a reason to be upset and start being treated immediately. It is enough will be periodic prophylaxis that allow to avoid in the future to reduce the density of bone tissue.
Comprehensive and full-fledged examination allows us to determine the total coefficient of osteoporosis diagnostics. More comprehensive answers to questions about what analysis on osteoporosis is called the most informative study where you can seek help from an experienced doctor. Do not tighten with the appeal to the doctor!