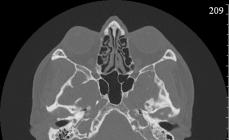
The temporal bone of the skull is a complex pair structure containing many anatomical structures having a tangled relief from a plurality of ducts, depths, hearing bones, inner ear, eardrum.
KT-anatomy of temporal bones
Near the pyramid of the temporal bone is located a saddle of a Turkish saddle, where an important endocrine iron is located - pituitary gland. The organ regulates the state of the endocrine glands. Computed tomography (CT) well shows the structure of the region, allows you to determine the size of the Turkish saddle, reveal the tumors, occasion, the inflammation of the pituitary gland.
The temporal bone is connected to the rolling jaw through the temporomandibular articulation. Arteries, nerve fibers are located near the region. Damage to the segment causes multiple pathology leading to inflammation of the internal and middle ear (otitis), violation of swallowing, inflammatory processes inside the esophagus, stomach.
CT temporal bones normally
Computed tomography of temporal bones in the norm shows the following anatomical structures:
- Smooth, wall rosary;
- Physiological width of the lumen;
- Sclerotic type of the structure of the cells;
- Normal pneumaticization;
- Soft detergers of the mouth of the hearing pipe;
- Clear visualization of auditory bones;
- Normal passage configuration;
- Clear smooth walls.
The CT-signs of bilateral secondary otitis with chronic flow are often combined with increased sclerotization, decrease in pneumaticization of the cells of the maternity process. Purulent, inflammatory processes of the region are well visualized on a computed tomogram.
CT temporal bones - what shows
X-ray computed tomography is appointed for the study of bones. Soft fabrics better analyzes MRI.
CT-signs of the pathology of the drum cavity:
- Assessment of the state of the walls;
- Visualization of neural structures;
- Analysis of vascular formations;
- Determination of the anatomy of the deputyid process, pyramids.
The middle ear is located near the brain shells, facial nerve, large blood vessels. Computer scanning allows you to clearly define the purulent-inflammatory processes of the middle ear (otitis).
Computed tomography of temporal bones clearly monitors tumor, traumatic damage. The neoplasms of vestibular and hearing units of small sizes do not lead to a drop of hearing.
Computer tomography shows the degree of mineralization (density of calcium salts), internal and middle ear replete. The deposition of sclerotic tissue is observed in chronic processes.
On computer tomograms are determined by tumors - osteomes, fibromes, angioma. The neoplasms are slowly growing, may be accompanied by hemorrhages.
Long purulent otitis leads to medium ear cancer. The tumor is malignant, has infiltrative growth, is characterized by the propagation of neighboring areas, is characterized by a tendency to spread to surrounding anatomical structures into lymph nodes.
Pathology leads to strong painful head syndrome, purulent bleeding, accompanying inflammation of the facial nerve. Timely CT allows you to determine nosology at an early stage, reduce mortality.
Any pathological changes in the temporal bone, the pyramids, the preceding process leads to a violation of blood supply. The high probability of the pathology of the microcirculation of the brain is due to the close arrangement of the brain arteries. Ingestion of the vessel of the purulent bunch, blood closure, embolos leads to a blockade of blood supply, the occurrence of a section of bleeding.
Indications to CT temporal bones:
- Internal selection;
- Falling hearing and vision;
- Traumatic lesions of temporal bones;
- Pathology of the temporomandibular joint (ENCH);
- Before prompt intervention.
Tomography of temporal bone is a rapid, informative way to diagnose most types of nosologies.
What is better than CT or MRI of the temporal area
The effectiveness of computer and magnetic resonance tomography of the temporal region differs significantly. The difference between CT and MRI not only in the physical basis of the method. Radiation irradiation of tissues in high doses does not allow using computer tomography re-over a short period of time.
Magnetic resonance tomography is harmless to human health in the absence of metal objects in the body. Modern innovative tomographs are able to track even the pathology of bone tissues. The price of the equipment is high enough so that peripheral medical institutions can acquire MP scanners.

Tumor of the metering glow on CT of temporal bones
CT with contrast also allows you to study arteries, veins, nerves, other vascular formations, tumors, measuring dimensions.
CT pyramids of temporal bones
Thickening in the middle of the temporal bone called the pyramid contains the anatomical structures of the middle and inner ear. The area includes many vessels, nerves. X-ray layered scanning of the pyramidal part of the temporal bone allows you to identify tumors, purulent infiltrates, pathological cluster of the liquor.
Purulent and bacterial inflammatory processes, bleeding inside the pyramid are well diagnosed after contrast. The procedure implies intravenous administration of the reinforcing drug, followed by the manufacture of layered sections. Each tomogram shows anatomical structures in a slice, but using three-dimensional modeling, you can create a spatial display of the object. The picture allows you to identify the smallest cavities, internal ducts, plan the course of operational intervention.
CT when Otitis
Bacterial inflammation of the middle ear leads to the amazing of the mucous membranes, the accumulation of pus inside the cells of the mastoid process, the eardrum. The long-term preservation of chronic inflammation leads to the exit of pus outward, the appearance of the perforation hole in the drumpatch. Pathology forms hazardous complications:
- Loss of hearing;
- Infiltration of the inner ear;
- Spreading of pus on the circulatory system;
- Destruction of the walls of the mastoid process;
- Destruction of inner cavities;
- Sigmoid sinus thrombosis;
- The development of abscess;
- Epidural hematoma;
- Empieme;
- Involvement in the inflammatory process of auditory bones with hearing loss.
The conclusion of computer and magnetic resonance tomography is often completed by the formulation of the diagnosis of "Mastoite". The error in the interpretation occurs due to the detection of aseptic fluid inside the maternity cells arising from the simple exudative otitis. It is possible to properly diagnose mastoids only after the detection of inflammatory damage to bone partitions.
Computer tomography of the temple bone
The presence of radiation exposure when using the method of computed tomography (CT) requires a thorough attitude to the application of a survey in a child. Only in the presence of dangerous diseases, the absence of effectiveness from the conservative treatment of mesotimpanum diseases, epitimpanum, hypothimepanum according to the testimony is performed by scanning children.
Epitiapanum is the upper part of the drum cavity, consisting of an auditory pass, the ear shell and the drum cavity. The inflammatory and purulent processes of the region are well detected after inspection of otolaryngol (ENT doctor). The need for computer tomography to diagnose the pathology of the region is absent.
Mesotimpaanum is the middle part of the drum cavity. The region consists of Eustachiyeva, the auditory pipe. The inspection area is not available, so the survey is carried out by radial methods.
The lower part of the drum cavity (hypothimepanum) can be studied only with the help of computer scanning. The department contains important anatomical structures - three semicircular channels (lateral, rear, top), snail, finver.
Otosclerosis on CT
The hereditary genetic disease - the otosclerosis occurs due to metabolic disorders. The exact cause of the disease failed. Morphological changes in pathology are accompanied by the growth of bone tissue with filling the cells of the maternity process. Resorption is due to the activity of bone cells - osteoblasts and osteoclasts. The destroyers are filled with fibers of the connective tissue. Sclerosis of the inner ear leads to hearing loss (conductive). In young people, nosology is characterized by the formation of a sclerotic focus near the front edge of the forever. The novice radiologist does not always detect changes. The process of bilateral, therefore it is adopted for an anatomical rate.
Choleateatom on computer tomograms
Tumor formation (cholesterol) consists of epithelial tissue, connective tissue fibers with an average ear. The danger of the disease lies in the sclerosis of the depository cells of the pyramid of temporal bone. Lor doctors believe that the rationality of the diagnosis of cholesteatoms with CT is not, since the part of the tumor is detected during the inspection. Three-dimensional modeling after computed tomography allows you to identify a small formation in the auditory canal at an early stage of development.
The CT cholesterol has a form of a soft formation with concomitant bone erosions.
Tomographic signs of cholesteatoma:
- Location inside an auditory pass;
- Soft education;
- Displacement of auditory bones;
- Erospanum wall erosive defects, lateral semicircular channel.
During the scanning, an additional finding can be other tumors of the temporal bone - hemangioma, osteoma, neurinoma, glomble formations.
Price CT of temporal bones
Experts are recommended to perform tomography of the temporal area after inflammatory processes, skull injury, hearing fall, suspicion of tumors. The price of surveys in Moscow varies from 2500 to 6,000 Russian rubles. A large range is determined by the type of equipment, the qualifications of doctors, the use or absence of contrast.
The cost of the service includes the need for anesthesia (child), recording results on an optical disk, the need to obtain a second opinion. Obtaining several radiologists' conclusions require patients with revealed inflammatory processes (chronic mastoid, otitis).
Where to make CT temporal bones in Moscow and St. Petersburg
Most of the Moscow clinics and St. Petersburg collected a "Unified Advisory Center". We offer readers to choose the optimal diagnostic center near the place of residence, next to the work. Sorting is carried out on dozens of parameters. Our partners have licenses, modern equipment, qualified personnel. The institutions offer not only CT head, neck and MRI services, but also a free preliminary consultation, a second opinion when deciphering the tomograms made in other establishments.
Alternatives to X-ray computed tomography in the diagnosis of pathology of the pyramids, the depositous cells of the temporal bones do not exist. Magnetic resonance scanning is used to determine the soft pathology. Turning to professionals, protects not only from unreasonable irradiation, but also from unnecessary financial costs.
The temporal bone is a pair component of a cranial box, which is distinguished by a complex relief and a non-standard form. It consists of three segments, the dysfunction of which leads to irreversible health consequences. The temporal bone is needed to protect the nerve components, the auditory apparatus and the large artery, it settles the work of the vestibular apparatus. During the problems of the characteristic zone, computed tomography of temporal bones is required.
General information about the procedure
CT temporal bone is a non-invasive diagnostic method, which allows you to estimate the structural and functional elements of the estimated focus of pathology. When using computed tomography on the temporal bone, X-ray is sent, which fixes the image of transverse sections. The position of the bone structure appears on the screen, the state of neighboring systems and tissues, presumptuous mutagenic zones (malignant tumors)
This diagnostic method can be carried out simultaneously with MRI to clarify the diagnosis, corrects medical prescriptions, allows you to determine the exact treatment scheme, increase the chances of the patient to recovery. The temple injury is one of the most common pathologies in which the clinical examination is difficult. CT and MRI with the help of sensitive equipment shows oncological processes, inflammatory diseases, abscesses and infectious damage, extensive disorders of vascular walls and anomalies for the development of bone structures.
Conducting MRI in such a clinical picture becomes auxiliary against the background of the main diagnostic method - CT of temporal bones. This is explained by the fact that the first procedure exactly visualizes the soft tissue on the screen, which contains hydrogen and fluid atoms. Since such a formula is somewhat different from bone structures, MRI is considered an ineffective method in the diagnosis of bones, and as an alternative it is desirable to use computed tomography. If there is a suspicion of the presence of malignant tumors, without MRI can not do.
Indications for the procedure
CT of temporal bones is shown in the following clinical paintings:

The doctor appoints a survey for effective treatment, but also does not exclude the implementation of the CT in order to effectively prevent.
Contraindications to conduct a procedure
CT temporal bones, as well as other non-invasive diagnostic methods, have their limitations, whose disruption leads to a sharp deterioration of general well-being, recurrence of the main diagnosis. So, restrictions apply to the following pathologies and features of the body:

If the CT of the temporal bones is shown in breastfeeding, the child is required briefly translate into artificial blends. According to numerous studies, the contrast agent is displayed with breast milk, penetrates through the placental barrier.
In most clinical paintings, doctors recommend holding CT using a contrast agent on the basis of iodine. It is necessary to get a clear picture on the screen, improves the visualization of bone structures. If even after such preparatory measures are doubts about the diagnosis, it is necessary to agree to the additional conduct of the MRI.
Preparatory measures and procedures
CT in separate clinical patterns is carried out using a contrast agent that requires preliminary preparation of a clinical patient. 5-6 hours before the procedure is fulfilled, be sure to refuse meals, and in 1-2 hours it is desirable and not to drink. It is also recommended to refrain from bad habits, avoid penetration into the body toxic and poisonous substances. When CT of temporal bones is carried out without using a contrast agent, there is no need for preparatory measures.

The description of the procedure makes it clear that the patient does not wait for a complex test. The procedure lasts 3 to 7 minutes, requires immobility of a clinical patient. The patient is offered to lie down on a special table, which is moving into the inner space of tomograph. Above the head rotates a special ring in a circle, while the movement of the couch is applied. Communication in the bilateral tomograph, therefore, when a discomfort can report its feelings with medical personnel, which observes what is happening through the glass.
If the patient moves during the CT of the temporal bones, the image on the tomograph screen will be blurred, fuzzy. In this case, it is difficult to determine the final diagnosis, it is required to continue the diagnosis, the re-use of this non-invasive method is not excluded.
Before holding the CT of the temporal bones, it is necessary to figure out the testimony from a doctor, as well as ask what is the price of the survey. On average, the range of rates varies within 2 - 3 thousand rubles, but it is important to remember that the contrast procedure will cost much more expensive (but the result is more accurate, the conclusion is informative).
Advantages of the procedure
Computed tomography of any bone structures is characterized by high sensitivity, guarantees the definition of the pathological process at an early stage.
If MRI studies in detail soft tissues, CT is more appropriate in the diagnosis of bone structures, durable biological materials.

The method eliminates side effects, if you clearly follow all the recommendations. Anomalies occur only if the intolerance of iodine prevails in the body, from which a contrast agent is made.
You can get a conclusion immediately after the procedure, head with him to the attending physician for a reliable diagnosis and adequate treatment scheme.
If we compare the cost of the procedure with the price of magnetic resonance tomography, then it is an order of magnitude lower, accessible to all patients.
Many patients captivates the speed of the session, so it does not have a long time to remain in a fixed position and morally suffer.
Before entering a contrast agent into Vienna, the doctor performs allergic tests than eliminating the risk of skin rash and accompanying its discomfort.
The list of contraindications is limited, with some clinical paintings (pregnancy, lactation) are temporary.
If the doctor recommended CT temporal bones, then it should be pre-figure out that it gives such a diagnosis that the results affect, and what are the consequences for the organic resource in a particular case. After such clarifications, it is recommended to agree to the examination and not tighten with the visit to the clinic. Perhaps such a delay can cost a patient physical activity, life.
In injuries of the head, complaints of pain in the temples, hearing impairments or vision, problems with the maxillofacial apparatus The attending physician (therapist, surgeon, the otolaryngologist) can send the patient to the CT of the temporal bones. The procedure is a transmission of X-rays and is an effective means of diagnosis. The survey results are displayed on the computer monitor.
This study resorts to check the effectiveness of the selected course of treatment or clarify the conclusion if other means of diagnostics are not informative. Computer tomography of temporal bone prescribe:
- in injuries and fractures;
- in cancer and tumors of unclear genesis;
- in diseases of the ear, discharge from ear channels, infections and bacterial lesions;
- with hemorrhages in the brain;
- in the presence of foreign objects in the ears;
- with a worsening of hearing and vision;
- with dizziness and headaches;
- before surgical intervention as a justification and to compile an operation plan.

Together with the ordinary study, multispiral tomography (MSCT of the temporal bone) is prescribed, which is characterized by the fact that during the examination the number of pictures in one approach increases, allowing you to obtain a multi-section, more accurate volumetric picture.
As contraindications, absolute and relative are distinguished. To the first:
- allergy to a contrast agent (on iodine-containing drugs);
- bronchial asthma in the aggravation phase;
- severe forms of renal or liver failure;
- metal implants in the field of research.
Relative contraindications include pregnancy and children's age, as well as inability to lie still and inadequate behavior during the study (in mental illness). In these cases, the survey is resorted if the risk of complications below the alleged benefit. Women whose children are on breastfeeding, will have to abandon breastfeeding for two days, as irradiation and contrast penetrates milk.
In computed tomography of the temporomandibular joint and the head, individual contraindication is Parkinson's disease. It is worth paying attention to the restrictions on the patient's weight - some devices are designed for weight up to 120 kg.
Preparation
Conducting procedures with contrast requires preparation. It lies in the failure of food 5 hours before the study. You can have a maximum of drinking water in 2 hours. It is recommended to refuse smoking and alcohol per day to normalize the state of the cardiovascular system and avoid dizziness and nausea. In some cases, the doctor prescribes allergothes on iodine, blood tests and urine.
Preparations for CT or MSCT of temporal bone without contrasting is not required. It is necessary to come to the procedure in loose clothes without metal elements, removing the earrings, piercing and other decorations.
Methodology
Depending on the complexity of the diagnosis and contrasting, the examination takes from several minutes to half an hour.
- The patient is placed on the back on the movable table. The head is fixed on the pillow, sometimes belts are used to prevent involuntary movements. If necessary, a staining substance is intravenously introduced.
- The table is moved inside tomograph, and the medical staff goes into another room to observe and register results. The active part of the apparatus begins to rotate around the head with a little noise.
- It is necessary to lie still so that the pictures are clear. The specialist may ask to turn his head or hold his breath.
- Then for 0.5-1 hours, a radiation diagnostic specialist is engaged in decoding the pictures.

The device is equipped with a two-sided communication system. When dizziness, itching, unpleasant and painful sensations, it is necessary to inform about it.
The decision on how often the procedure can be passed, takes the attending physician, based on the severity of the patient's condition and the course of the disease. When CT dose of irradiation load is small, but the study is considered to be safe 1 time per year. If necessary, the frequency increases to 2 times a year, but not more often.
Axial, front and sagittal projection
Depending on the direction of X-ray rays to the study plane, 3 standard types of projections are distinguished:
- axial (transverse plane);
- frontal (parallel plane of the forehead);
- sagittal (along the annex axis).
There are also atypical projections, they help detail the identified changes in hard-to-reach areas.
Due to the integrated use of standard and atypical projections, CT and the MSCT of the temporal bone are of high-precision.
Using contrast
If you want to identify the condition of soft tissues and blood vessels, iodine-containing preparations are used, which are introduced intravenously at different stages of the procedure.
Iodine makes visible soft fabrics, shells and education. For this, the contrast is introduced a few minutes before the examination or during it, making a number of shots before.

The introduction of contrast can be associated with side effects - nausea, dizziness, itching. If there is allergies to seafood, the likelihood of an acute response to contrast is large. In this case, an alternative to computed tomography is MRI without the use of contrast.
To kid
Children's age is a relative contraindication to radiation diagnosis. However, the benefits of the high efficiency of the method for the detection of foci of inflammation, tumors and injuries exceeds the negative effects of irradiation. Therefore, in the presence of justification and in emergency cases, it is allowed to carry out the CT of the temporal bones of the child (allowed for children from birth).
Preschoolers and older children pass the procedure in normal mode. If they can not save immobility, they are injected into a medical sleep or provide general anesthesia.
Preparation for the study does not differ from the preparation of adults. When tomography without contrast, you just need to come to the procedure, removing the earrings and other decorations, dental plates, informing the doctor about metal implants if they are present. With the introduction of iodine-containing substances, it is impossible to eat in 5 hours, drink for 2 hours. It requires data on the existing allergies (it is better to carry out allergos in advance).
What shows CT temporal bones
CT temporal bone is an effective method for determining pathologies, anomalies and characteristics of the anatomy of the skull. This head area has a complex structure, includes bone structures, medium and internal ear, Eustachiyev pipe, and brain shells, large vessels and auditory nerve. With such a close location, the symptoms of the disease may be non-obvious, and other methods of diagnosis are non-informative. Translucent X-ray helps to obtain images of internal structures with cuts with a thickness of up to 1 mm.

The tomography of the temporomandibular compound (ENCH) of the articular without contrast is prescribed to detect fractures and cracks of this department and changes in bone structures. With contrasting, the procedure makes visible:
- tumors and metastases;
- abscesses;
- vessels;
- hematoma;
- liquid in middle ear.
CT and MSCT - modern, relatively harmless types of diagnostics based on X-ray radiation, with which it became possible to determine pathological processes at the very beginning of their development. It helps to make treatment more efficient and monitor the selected course.
Modern non-invasive diagnostic methods are very important and informative in the treatment of hearing organs and soft nose tissues. CT or computed tomography of temporal bones makes it possible to obtain data on the state of the internal and middle ear.
The bone of the temporal area is quite complicated. Inside there are structures of the organ of hearing. Nearby there are auditory nerves, the brain shell, the circulatory network. Anatomical zones are very close, so with standard diagnostics it is difficult to determine the pathology.
The performance of computer tomography of temporal bones allows you to get information about the dissemination of changes and the localization of the inflammatory hearth. CT (temporal bone) is needed to form an accurate diagnosis and monitoring of pathology in the process of therapy. CT temporal bone reveals anatomical structure, norm and anomalies. Pathology cause infringement of blood supply, inflammation of the facial nerve, dizziness and poor well-being.
If necessary, CT of depository processes are carried out. The procedure is based on the passage of X-rays through the soft structures of the body. The monitor displays the resulting digitized image of the desired sites. Snapshots are performed in various angles, which allows the diagnostic to visualize the slightest changes in organic tissues and cavities. They are clearly visible as an auditory bone, snail inner ear. Computed tomography of temporal bones does not give excessive radial load and safe for humans.
When a survey is appointed
Indications for the procedure are different. An indispensable study in the presence of anomalies for the development of the inner ear. The bone is also investigated. It is especially important to obtain an image of an affected area during injury.
MSCT (tomography) of temporal bones like CT is shown at:
- changes in the eardrum;
- purulent discharge from ear;
- loss of hearing;
- hemorrhage;
- fracture of temporal bone;
- pathologies of outdoor auditory passes;
- study of the nerves of the temporal zone;
- otitis;
- degenerated changes in temporal bone;
- otosclerosis;
- abscess;
- metastastes.
The study is important to go through the on the eve of operational intervention, as well as to identify the effectiveness of the appointed therapy. Tomography is shown in any inflammatory process affecting the bone. The method determines the localization of the hearth and the degree of illness.
What can show CT temporal fractions
The temporal bone reliably protects the inner ear from damage. It is adjacent to chewing and hearing aids. With a worsening of hearing or vision, it is important to pass the CT of temporal bone. X-ray shows the slightest pathological changes in the surveyed plot.
Lining the three-dimensional image of the zone surveyed helps to visualize:
- eardrum;
- the structure of the internal structures of the ear;
- mastoid;
- otosclerosis;
- fracture;
- abnormalities of the structure;
- arteries' Patency;
- hemorrhage;
- tumor;
- state of vessels;
- otitis.
Vices may be congenital and acquired. CT temporal bone shows all the features of pathology, its course and distribution. The procedure shows the abscess of soft tissues in their swelling, the impaired passability of the circulatory network, changes in the bone and nearby structures, the promotion of metastases during the tumor. With the help of CT temporal bones, vascular formations are visualized, neural structures, the state of the walls. Scanning without problems determines:
- the presence of purulent inflammation;
- osteoma;
- calcium salts densities;
- fibromo;
Planning the CT of the temporal bone, ask what exactly shows the device, at the doctor. Areas of research using tomograph are different. Tomograph - Equipment number one for differentiation of diseases of the temporal part.
- the bone has the boundaries of smooth and clearly defined;
- the physiological parameters of the lumen do not have deviations;
- cells have a sclerotic structure;
- the mouth of the auditory pipe is not amazed;
- the passage configuration does not have deviations.
In pathology, signs of otitis are visualized. Sclerotization is excessively raised, pneumatization of the cells of the process, on the contrary, is reduced. It is clearly visible to the presence of pus in organic structures, degree of lesion, inflammation localization. Bone can have anomalies or a fracture.
How is tomography and preparation
Equipment is a large camera with a retractable couch. The patient is placed on it, its limbs are firmly fixed, and the table drives inside the apparatus. There are tomographs of open and closed species. During the entire session, the patient is in a fixed state - any movement can lead to strong distortion of scan results.
Waves that reproduce the apparatus pass through the soft organic structures of a person. It does not hurt and not dangerous. All that may feel the patient in the session process is a small discomfort. It is associated with the inability to move and with stay in a closed space. That is why people suffering from claustrophobia cannot endure in the diagnostic equipment capsule.
About the patient's condition, the doctor can recognize through the negotiation block. It is inside the capsule and allows the connection between the doctor and the surveyed. The temporal bone scanning does not take much time - the session lasts about 25 minutes. Spiral 16 section tomograph allows you to reduce the study time up to 15-20 minutes. When the study begins, the patient must remain motionless. 
On the eve of the upcoming scanning, it is important not to overload the stomach of heavy food. Under the ban fat and fried dishes. The session is conducted on an empty stomach. It is undesirable to drink even liquids. Before the start of the procedure, you must take a shower, put on comfortable clothing without metal fasteners and buttons. It is impossible to use decorative cosmetics. CT temporal bone in a similar case is distorted. To the picture turned out to be clear, do not apply makeup. From the ears it is necessary to remove the earrings, the glasses, clock, belt are eliminated. There should be no metal elements and jewelry on the body.
Who can not do
Non-invasive research cannot be carried out during pregnancy, lactation. It is also impossible to perform a session to people suffering from claustrophobia and mental illness.
In renal failure, scanning is not performed using a contrast agent. The drug is excreted by the kidneys, and a poorly working body is not able to cope with the desired task.
From contraindications also:
- alcoholic or narcotic intoxication;
- some heart defects;
- the presence of a pacemaker;
- the presence of non-coordinate dentures;
- the presence of implants in the body.
Computed tomography - a modern method, which is constantly improved. Modern tomographs are equally different in their capabilities from the first samples. With this diagnosis of temporal bone, you can distinguish pathology at an early stage. But do not do CT too often. The procedure is performed according to the testimony not to expose themselves once again with radial load.
MSCT temporal bones

MSCT temporal bones - multi-section X-ray tomography, performed to study the structure of paired bones located in the side sections of the skull. The temporal bone has a complex structure: it is involved in the formation of the ENCH, the arch and base of the skull, the organ of hearing and equilibrium lies, the nerves and vessels pass through its channels. In this regard, any pathological processes of this area can lead to a violation of the most important functions. MSCT allows non-invasive and high-speed to detect morphological changes in the scales, drum part and the pyramid of temporal bone, external auditory passes, middle and inner ear, bone channel systems. The testimony for the designation of the MSCT of the temporal bones can be injuries of the area, inflammatory processes (otitis, mastoid), decrease in hearing, vestibular disorders, aurora of Likvorea and MN. Dr.
The temporal bone has an extremely complex structure - in its thickness there is a huge amount of cavities and canals, the walls of which are formed by thin but dense bone structures. The contents of these formations are hearing and equilibrium organs, nerves and vessels, some cavities are simply filled with air and are inserted from the inside the mucous membrane. With traditional radiography, all these anatomical formations are superimposed on each other, forming a picture complex for identifying and diagnosing. More advanced radiographic techniques (such as simple computed tomography) allow you to obtain more information about the structure of the temporal bone, but a significant thickness of the sections (about a few millimeters) does not allow the opportunity to form a complete picture of its structure.
MSCT of the temporal bones is the result of the development and improvement of the usual computed tomography. When conducting the procedure, the radiation source and detectors are moving not along the radial trajectory, but by spirals - due to the simultaneous movement of the X-ray tube in a circle and the investigated area perpendicular to this plane. The epithet "Multispiral" This study was due to the fact that it uses several rows of detectors at once, which allows for one cycle of the X-ray radiation source to obtain a plurality of sections. Currently, the machines for MSCT temporal bones, containing 64 sensors, separate diagnostic centers have equipment from 128 and even 256 sensors.
Due to the set of factors - a large number of sections for one cycle, spiral movement of the source and radiation receivers relative to the area under study, special processing of the data obtained - the MSCT of the temporal bone is a very accurate study method. It allows you to form 3D-models of the pyramids of temporal bones with all the cavities and structures, as well as produce their sections in any plane. The use of intravenous contrast further increases the information content of the MSCT of the temporal bones, especially in terms of studying the soft contents of their cavities. Almost the only decent competitor for this diagnostic technology is magnetic resonance tomography (MRI). Both MSCT, and MRI have their advantages and disadvantages - computed tomography (without contrast) worse visualizes soft tissues and creates a certain radiation load on the body, but at the same time it reflects the structure of bone tissue much more accurately. MRI of the temporal bones shows more detail the structure of soft tissues and does not have a radiation impact, but its conduct is impossible in the case of a patient with metal implants (crowns, brackets, orthopedic equipment).
Indications
The reason for the purpose of the MSCT of the temporal bones is most often the signs of the lesion of hearing or equilibrium organs. The symptoms of such pathological conditions may be pain in the ears and the temporal area of \u200b\u200bthe head, discharge from the ear, unfortunate dizziness, nausea. As a rule, these manifestations have an inflammatory or tumor nature, the pathological process is localized in the region of the middle ear or semicircular tubules - structures located in the cavities of the pyramids of the temporal bones. Pathological foci is perfectly diagnosed even during a simple MSCT of the temporal bones, contrasts can be made to obtain a clearer diagnostic picture.
Another common cause of the administration of the MSCT of the temporal bones is injuries of the head, which are fraught not only by damage to the hearing organs and equilibrium, but also vessels, nerves and brain. Often the results of this study, made after the cranial and brain injury, are becoming a reason for emergency surgery - for example, in order to stop intracranial bleeding. In this case, it is possible to re-conduct the MSCT of the temporal bones - to assess the results of the operation and control the recovery process. Sometimes the indication for this diagnostic study are various disorders in the movement of the lower jaw - then the object of study becomes the temporomandibular joint.
Contraindications
Contraindications for the MSCT of the temporal bones are a little, as a whole, they are similar to that with traditional computed tomography. The absolute contraindication is pregnancy, since this diagnostic study is associated with radial load, negatively acting on the development of the fetus. Relative contraindications can serve as children's age and the presence of neurological diseases with hyperkinases, since during the MSCT of the temporal bones it is very important to maintain the full imperativeness of the head to create a clear "picture". If you need to use contrast contraindications are renal failure and intolerance to the contrasting substances.
Preparation for MSCT
Special preparation before the MSCT of the temporal bones is not required. This study, as a rule, directs a otolaryngologist or neurologist, based on the patient complaints and the results of some other diagnostic procedures (audiometry, neurological tests). When using contrast on the eve of the MSCT of the temporal bones, the patient is desirable to refrain from meals and medicines (if the cancellation of medicines is necessary and approved by a doctor). In severe and emergency cases, for example, during convulsions, a sedation (introduction into anesthesia) can be met as a result of the acoustic brain injury. This is necessary to immobilize the patient and obtain a clear picture of the structure of temporal bone.
Methodology
The MSCT of the temporal bones itself is very similar to the usual computed tomography - the patient is stacked on the table of the apparatus, which under the control of the doctor moves to the "Ring". As a rule, the MSCT holds much less time - 64 or 128 sensors allow only one cycle (10-15 c) to perform a complete study of the temporal bone. For the processing of the results obtained, a few minutes are leaving, after which the images of the required sections (depending on the objectives of the study) are recorded on a disk or a special film. The interpretation of the results is engaged in a radiologist and a specialist who sent a patient to the MSCT of the temporal bones. In this case, the structure and integrity of bones and soft tissues, the presence or absence of signs of inflammation or tumor process is estimated.
Interpretation of results
The most common cause of the designation of the MSCT of the temporal bones is inflammatory processes in the field of medium and internal ear, as well as equilibrium organs. With an average ottitis, a thickening of the drum mucosa is observed, it can determine the exisudate. With severe purulent course of the disease, the melting of the bones of the middle ear can be detected, as well as the walls of the drum cavity with a breakthrough of pus into the cavity of the skull. The labyrinthitis or inflammation of the inner ear is accompanied by an edema of the organ, which is registered on the MSCT of the temporal bones. Tumor processes can lead to a change in the shape and sizes of the cavities of the pyramid of temporal bone, a wide vascular network of neoplasms is detected in contrasting.
Quite often, the MSCT of the temporal bones is produced during brain injuries to establish the degree of damage. Since bone fractures can lead to a violation of the integrity of blood vessels, squeezing the nerves passing through the channels, or injury to the brain, the result of the study often becomes a reason for the surgical operation. At the same time, the data of the MSCT of the temporal bones allow the neurosurgeon to determine exactly which area is damaged - therefore, it is possible to plan the course of operation in advance, reduce its duration, reduce the degree of injury to tissue.
Cost of MSCT temporal bones in Moscow
The scan price depends on the type of equipment used, while the main pricing factors are the number of detectors in the device and power of the computer. A significant role in the formation of the cost of the procedure plays the need to use contrast. So, the price of MSCT without contrasting is almost twice as low as with the use of a contrast agent. A planned diagnostic study is more accessible in private medical centers, while in state clinics MSCT is primarily carried out on emergency and vital indications (for example, during crank-brain injury), in other cases a preliminary entry is needed and sometimes a long time expectation. A detailed conclusion of a specialist and record the results on electronic media is also factors that increase the cost of the study.