Osteoporosis is a disease that develops against the background of a disorder of the structure of bone tissue and reducing its mass. As a result, the fragility of bones increases and the risk of fractures increases significantly. In the world among the diseases of non-infectious nature on mortality and disability, this disease is in fourth place after diseases of the SCC, oncopathology and diabetes mellitus.
With the arrival of a climetheat period with bone fabric problems, a third of women is facing around the world. In addition, osteoporosis is diagnosed for each second who reached the seventy-year-old age. In order to diagnose this disease, the bone densitometry is widely used. Early diagnosis is indispensable for the start of timely treatment. But the purpose of this procedure causes patients a number of questions: Densitometry - what is it? What are its views? How is the densitometry and what shows?
Procedure varieties
Densitometry or osteoodensitometry is an instrumental method of diagnostics, which makes it possible to evaluate how much and in what quantity demineralization of bone tissue. To do this, pay attention to a number of indicators, including relative density, spatial structure and the thickness of the cortical bone.
The mechanism and principles of manipulation can be very different, so research is divided into 3 types:
- ultrasonic densitometry;
- x-ray densitometry;
- photon absorptiometry.
As a rule, with suspicion of osteoporosis, we first assign ultrasound diagnostics, and if suspicion is justified and some clarifications are needed, then they are resorted to the help of X-ray or radioisotopes.
To confirm osteoporosis T-score in decoding should be below 2.5
Uz Densitometry
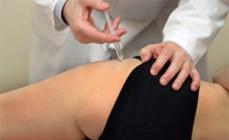
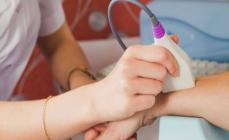
Ultrasound densitometry is an indirect determination of bone mineralization. The ultrasonic wave passing through the fabrics with different density is distinguished by the speed of movement. The densitometer apparatus produces a certain frequency ultrasound, which is passed through the bones in a given area and is captured at the output of the registration sensor. Ultrasound densitometry, despite lower information capabilities, is used quite often. This is due to its full security, the speed of execution and the ability to pursue such a diagnosis without the direction of the doctor and additional surveys.
X-ray densitometry
Mineralization of bone tissue is calculated according to the developed algorithm on the surveyed area, which was exposed to X-ray rays. There are several types of X-ray densitometry:
- Two-energy densitometry. This method involves passing a pair of X-rays. One passes through the bone tissue, the other in soft and their results are mapped. The measurement is made, repulsted from the fact that the higher the mineralization of the bones, the lower the permeability of X-rays. This method is used to survey the spine and femoral bone.
- Peripheral densitometry. The principle of measuring the density is no different, as in the case of a two-energy technique, but with smaller doses of radiation load. This method is suitable for estimating bone limb tissue, but we are weak to study the state of the spinal column and the femoral bone. Use it mainly in order to control the therapeutic process.
- Method of quantitative computer tomography It is also carried out under the influence of ionizing irradiation and allows you to obtain a volumetric image of the bone structure. It is used extremely rare, due to the high degree of ionizing irradiation, which is subjected to the patient and the price category of the procedure.
Due to the increased radial load, X-ray densitometry do not conduct pregnant and nursing women, and in children's practice is used with great caution.

Densitometry can be made in most state clinics or diagnostic centers
Photonic absorption
This method is based on photon beams. They are passed through bone tissue and, depending on how much photons were absorbed by the calculation of bone mineralization. The process uses low doses of irradiation. There are 2 types of photon absorption:
- Monochrome densitometry - this method is used exclusively for the diagnosis of mineralization of peripheral bones.
- The dichromic method is used to diagnose the mineral density of the spinal bones and hips.
If you compare X-ray densitometry and photon absorption, then the first resolution resolution is significantly higher through the use of more powerful radiation. In addition, this method is more accurate and scanning is much faster.
Indications for holding
Diagnosis of osteoporosis before its symptoms occur - this is the main indication for conducting densitometry. This procedure is recommended to carry out at least 1 time in 2 years such groups of persons:
- in order to prevent anyone who has reached 50 years;
- bad heredity (close relatives suffer from osteoporosis);
- female representatives after the onset of the menopausal period;
- against the background of long replacement hormone therapy;
- patients observed in endocrinologist (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency);
- after the fear of the neck of the hip aged 40 years;
- when manifest primary symptoms of osteoporosis;
- incorrect power supply for a long time.
Indications for this procedure in children can determine the endocrinologist, rheumatologist or traumatologist. Most often, the following pathological conditions may be served for such a survey:
- continuous reception of hormonal drugs;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the digestive tract, the pulmonary-intestinal form of fibrosis;
- diseases affecting connective tissue and vessels;
- pronounced pulmonary and renal failure;
- dwarfism (pituitary nanism);
- syndrome, accompanied by the insufficiency of the function of the genital glands and a violation of the synthesis of sex hormones;
- prolonged finding a child in a fixed state;
- pathologies of the musculoskeletal system due to genetic factors;
- fractures in history.

Dwarf - testimony for diagnostics
Bone densitometry allows a specialist to determine the decline in the mass of bone tissue at the initial stages, when even about 2% is still lost. This is a very good indicator for early diagnosis against the background of standard X-ray pictures that detect pathology if the third part of (or more) total bone mass is affected. And this already talks about the irreversibility of processes and the high risk of developing serious complications.
Areas of research
Today, the analysis of a densitometric study is the "golden" standard, and it is recommended WHO in order to confirm the osteoporosis in a patient. Densitometry of the entire body or individual parts of the musculoskeletal system can be performed.
Ostoseodensitometry of the axial skeleton (spine) is carried out from the first to the fourth lumbar vertebra using a special sensor, which measures the degree of absorption of undergoing X-rays, and builds a graph. Sometimes it is not possible to measure all 4 vertebrae, so three or two can be satisfied.
The femoral bones are inspected as follows. X-ray rays can be scanning the area of \u200b\u200bthe hip joint. More often, measurements are carried out on the left hip, but the right thigh also gives an equal result. The 5 parts of the hip joint are investigated: its neck, the top end of the body of the femoral bone, the interstate region, the triangle of the Ward and the upper part of the femoral bone.
The bones of the forearm - the measurement of the mineral density of the bone is carried out on a passive hand, as in the radial bone of the dominant hand, the bone mineral density is higher than about 3%. A special value is the indicator obtained at the point, which corresponds to 1/3 of the radial bone length. If the procedure is conducted by a child or adolescence, then preference gives the research of the vertebrae in the lower back area.
At the same time, the procedures are trying to perform as quickly as possible and with a minimum dose of ionizing irradiation. After computer processing, the bones are assigned a different score in points.
Preparation and methodology
Ultrasound densitometry does not require absolutely no special training. In the case of radiation procedure, the doctor will explain the patient as it should be properly prepared. 24 hours before the planned procedure, it should be refused to receive preparations that contain calcium. It is necessary to report to the diagnosticity, if the patient has a relatively recent radial study with the use of a contrast agent. It is necessary to tune in that during the procedure to be the most fixed and retain, specified by the doctor, pose.

It is important to abandon calcium-based medicines.
By time, the examination, as a rule, takes 30-40 minutes. The surveyed is asked to set properly on the diagnostic table under which the radiation source is located, and the device fixes the result. With a stationary examination, a special sensor is moved along the body, it freezes the levels of radiation, tolerates computer equipment, analyzes and outputs the result.
If equipment consisting of one block is used, then the examined part of the body is located in a special machine, and the result is issued after processing a computer program. To improve the quality of the image, the limb or patient can be recorded not to breathe some time. Having understood what densitometry is, it becomes obvious that the survey should seriously think about all those who are subject to factors that increase the likelihood of osteoporosis at any age.
One of the most reliable diagnostic methods is a disease accompanied by a decrease in the bone mineral density - as well as a method that allows to assess the quality is a densitometry. The fact that it is for the study by which categories of patients is shown and how contraindicated, as well as about the types of densitometry and the methodology of it, we will talk in this article.
What is densitometry and what kind of types
Densitometry is a non-invasive method for quantifying the mineral density of bone tissue. This study is carried out in specialized state and private medical and diagnostic centers. The procedure is absolutely painless for the patient, does not require anesthesia.
There are 2 types of densitometry: ultrasound and X-ray.
Ultrasound densitometry
It is a difficult diagnostic method. Allowed to repeated use in pregnant women and nursing mothers. It is carried out using a portable densitometer, which measures the rate of passage of ultrasonic wave through bone tissue. The speed indicator is recorded using a special sensor, the data from which is entered into the computer, where the system is processed, and then displayed on the monitor. Object of study: most often, the heel bone.
The advantages of ultrasound densitometry is the speed of the diagnostic procedure (as a rule, the time spent on it does not exceed 15 minutes), painlessness, lack of toxic effects on the patient's body. In addition, this test in material plan is available to most patients.
Used, as a rule, as the primary diagnosis of osteoporosis, in the case of its detection to perform the most accurate diagnosis, it is recommended to conduct a more specific study: X-ray densitometry.
X-ray densitometry
A more accurate study method rather than ultrasound densitometry. Its essence is to determine the degree of weakening X-rays when passing them through the thickness of the bone tissue. This indicator is estimated using a special apparatus. The latter then, following the algorithm, calculates the amount of mineral substances that met the X-ray ray through the bone path.
The object of the study during the conduct of X-ray densitometry can be a lumbar spine, a ray-tunny joint, femoral bone, especially its top department, completely all skeleton or separate parts.
Since this type of densitometry implies a certain dose (albeit minimal) X-ray, which is known to have a toxic effect on the human body, it is not recommended repeatedly for a short period of time. For the same reason, he is contraindicated with certain categories of patients, in particular, pregnant women and women, nursing toddler breasts. In addition, a very expensive equipment is needed to carry out this type of densitometry, which are allowed only in specially designed cabinets for this study. All this makes X-ray densitometry inaccessible for the basic number of patients using diagnostic.
Who shows densitometry
This study must be periodically (at least once every 2 years, on the recommendation of the doctor - and more often) to undergo the following categories of patients:
- women in the period, especially in the case of her early offensive;
- women older than 40 years old and men older than 60 years old;
- women who suffered admexectomy (that is, those whose ovaries are removed);
- persons suffering from parachite glands;
- persons who have happened at least one bone fracture due to a minor injury;
- persons over 30 years old, close relatives of which suffered osteoporosis;
- persons accepting for a long time drug preparations contributing to the washing of calcium salts from bone tissue (, anticoagulants, oral hormonal contraceptives, diurendic, psychotropic, anticonvulsant drugs, tranquilizers and others);
- persons abusing, as well as smokers;
- persons suffering (leading a low-wear lifestyle);
- persons of low growth with low body weight;
- persons who comply with various diet, which are fans of the medical starvation system;
- persons regularly experiencing intense, exhausting physical exertion.
To whom Densitometry is contraindicated
Ultrasound densitometry - a safe study, contraindications to which does not exist. The radiological method is not recommended during periods of pregnancy and lactation.
How to prepare for densitometry
 Special preparation for research is not required.
Special preparation for research is not required. If the purpose of the study is the primary diagnosis of osteoporosis, it should not be taken to take calcium preparations or other means that contribute to the increase in calcium content in the blood.
Special preparation for densitometry does not exist. Clothing on the patient should be comfortable, without lightning or metal buttons. If there are any metal jewelry, it is necessary to remove them before the examination.
If a woman who is appointed densitometry is pregnant, she should definitely prevent his doctor about it.
How does research passes
Ultrasound densitometry is carried out using a portable monoblock device. The studied part of the body is more often the heel, less often a finger or forearm, is placed in a special niche located on the device. For a short period of time - as a rule, 2-3 minutes - the device determines the speed of the passage of ultrasound through bone structures and processes the results, after which it issues them to the monitor of the computer attached to it.
X-ray densitometry is carried out using stationary equipment. The patient falls on a special soft table, while the X-ray generator is located under it, and the image processing device is top. During the study, it is impossible to move - to reduce the risk of blurring the picture, the doctor asks the patient to hold his breath for a while. When the patient is located in the desired posture, the "sleeve" with the reading device smoothly drives over it, at this time the device generates an image and sends it to the computer.
How to decipher the result of densitometry
In fact, the diagnosis of osteoporosis is exhibited on the basis of an estimate of 2 indicators obtained as a result of a densitometry - these are T- and Z-criteria.
T-criteria are obtained by comparing the resulting values \u200b\u200bof the bone density of the surveyed with the average normal bone density of women of 30-35 years.
The Z-criteria is obtained by comparing the dysnity of the bone of the person being examined with an average normal value of the bone density of its age group.
Unit Density Density - SD.
Values \u200b\u200bof norm and pathology:
- T-criterion is normal - from +2.5 to -1;
- When osteopenia - from -1.5 to -2;
- With osteoporosis - from -2.0 and below;
- With severe osteoporosis - less than -2.5 in combination with at least one bone fracture resulting from a minor injury.
As for the Z-criterion, if its value is too high or too low, this is an indication for additional surveys.
Thus, ultrasound or X-ray densitometry are diagnostic methods to determine the degree of mineral density of bones. It is necessary that the osteoporosis diagnosis is diagnosed in a timely manner, thereby preventing its formidable complications. Because this study is quite new, today it is not held everywhere - you should learn about the nearest center for the osteoporosis diagnosis of your attending physician.
Densitometry bones - This is a modern non-invasive method for determining bone density, which is performed for the diagnosis of osteoporosis. With this disease, the bones decreases the content of minerals (mainly calcium), which is why they become more fragile. Osteoporosis is the greatest danger for the spine and neck of the thigh, since fractures in these places are fraught with the most severe consequences.
Description of the procedure
What is this procedure - densitometryEach woman in postmenopausus should know, since during this period the most likely the likelihood of osteoporosis. Such a study makes it possible to identify it efficiently and absolutely painless in the earliest stages.
Densitometry refers to instrumental diagnostic techniques, and allows you to determine the density of bone tissue, more precisely, to make it a quantitative and qualitative analysis.
Distinguish densitometry ultrasonic and x-ray. At the heart of two these methods, there are different principles of operation, and various equipment is used. Sensors are used to read indicators, after which the data is transmitted to a computer for computing:
- relative bone density;
- the thickness of the cortical layer;
- architectonics (spatial structure) and other parameters.
Equipment for conducting a densitometric examination can be stationary, with a table and sleeves. It is commonly used to explore the spine, as well as bones and joints of the pelvis.
Also used monoblock equipment in the form of a small device that allows you to scan brushes, feet and other separate joints and bones.
X-ray densitometry
At the heart of the X-ray densitometry of the bones is the ability of X-rays to pass through soft tissues, lingering in the dense structure of bones, for which the high concentration of calcium salts and other minerals is characteristic. Based on the absorption rate of X-rays with bone tissue, experts calculate the degree of mineralization of various sections.

X-ray densitometry It is considered more accurate than ultrasound. It is held on a stationary table with a "sleeve", where the patient is placed on 10-30 minutes.
During the procedure, the spine or its departments, hip and wilderness or entire skeleton are examined. The technique is very accurate, but it is not possible to apply it in all cases: for example, pregnancy is a contraindication for conducting.
The cost of the procedure is from 1300 to 3000 rubles, it is determined by the scope and type of clinic. If there is a need to carry out a combined densitometry using a computer tomograph (CT-densitometry), then the cost will amount to about 5,000 rubles.
Such a densineometry on its method is similar to X-ray, but its accuracy is lower. It is considered an indirect method for determining the density of bones. Ultrasonic waves with different speeds pass through bone tissue areas with different density. The process is registered by the sensor, processed and in the form of data is provided by a specialist for analysis.
The cost of such a type of examination lies within 700-2000 rubles.
Despite the lower accuracy of the results, this method is also used quite widely, which is due to its absolute security, speed and possibility of execution without additional surveys. The procedure lasts from 5 to 15 minutes and can be carried out for pregnant and nursing.
Indications
Densiometry is carried out with suspicion of osteoporosis, as well as a prophylactic examination associated with this disease.
This type of survey is used to determine:
- The number of minerals in any of the bones or in the whole skeleton.
- The overall state of the spine.
- The presence of osteoporosis or osteopyation (a disease characterized by a small decrease in calcium content in bone tissue), the degree of development of pathology.
- Bone fractures and vertebrals.
That is, to pass densitometry makes sense for any person who is exposed to risk of development of osteoporosis. This is especially true of people subject to risk factors.
The list of these factors is presented:
- Violations of metabolism.
- Pregnancy, especially multiple pregnancies.
- Spinal diseases (spondylolisthesis, osteochondrosis), injuries.
- Endocrine diseases - hypothyroidism, diabetes, pathologies of parachite gland.
- Long-term reception of hormonal and other means of calcium.
- Some neurological disorders.
- Repeating fractures.
- Rheumatism.
- Defective nutrition, frequent observance of strict diets.
- Low body weight, alcohol and smoking abuse.
Densitometry of the lumbar spine and neck hips It can give a forecast for a fracture for 10 years, it can also be used to assess the effectiveness of the treatment applied.

When conducting such a survey regarding a child, it is possible to determine whether the calcium and phosphorus can be solved in its body so that the children's body can cope with the intensive growth of bones.
Number of calcium in the bones after 30 years begins to decrease with time, so approximately from 40 years old You need to control this indicator.
How often can Densitometry do? It should be carried out once every 2 years. Thanks to screening surveys, osteoporosis can be revealed in a timely manner and cure it. Such survey mode is recommended for women older than 30 years, which have close relatives subject to osteoporosis. Men must be examined for the purpose of prevention, starting from 60 years.
How to prepare for the procedure
Preparation for densitometry implies the execution of simple rules:
- During the day before the procedure, it should be abandoned by taking drugs containing calcium and phosphorus, as well as from the use of rich in calcium products (cheese, cottage cheese).
- A week before the procedure, you cannot conduct an MRI or CT with contrast, as well as isotopic scanning.
- The examination should not be sent to clothing with metal elements (zippers, rivets, buttons), which may affect the information content of the results.
- Getting Started Procedure, you need to remove the clock, hide in the bag mobile phone.
How made densitometry
When performing X-ray densitometry, the patient is placed on the table, which is equipped with a stationary machine, after which the specialist comes out of the room. When examining the spine to maintain the legs, a special stand is used.

In case of inspection of pelvic bones, legs are placed in a curly bracket. After that, the sleeve of the machine moves, while a series of pictures is made, and the data is transmitted to the computer.
Movement during the procedure is prohibited, if only such a team does not give a doctor. He can also ask the patient about breathing delay.
How do ultrasound densitometry? In this case, the patient lies on a medical couch, and the doctor performs an ultrasound procedure using a special nozzle with a sensor. Both types of research are absolutely painless, and are performed fairly quickly.

In this way, any region can be examined: the lumbosacral spine, the femoral region, the heel bone, etc.
Uzi-densitometry No contraindications. X-ray Strictly prohibited for pregnant women and nursing, and children are being done in case of acute necessity.
How to decipher the results of densitometry
Of all the results, which shows densinometry, the most important are:
- The density of bone tissue (the indicator "T") compared to the norm for young people in points. The norm is considered to be 1 point and higher; At 1-2.5, they speak osteopenia, less -2.5 - osteoporosis is diagnosed.
- The density of bone tissue compared with the norm for a certain age group (the indicator "Z"). This indicator should be in the specified borders by the ages.
The state of the bone system depends largely on the density and structure of the bones. One of the diagnostic methods to identify changes in this tissue is a densitometry. The survey is carried out using X-ray or ultrasound radiation. The procedure is painless and takes some time - from a few seconds to a few minutes. X-ray densitometry is the most versatile and accurate way. The examination requires minimal patient preparation.
- traditional radiography;
- scintigraphy;
- photon densitometry;
- x-ray densitometry (abbreviated in English DXA or DEXA);
- ultrasonic densitometry;
- quantitative computed tomography (Qst-densitometry, CT);
- two-energy CT, three-dimensional DXA analogue. This is the most modern method for the diagnosis of osteoporosis, which has not yet been extended to be widespread.
- lower measurement accuracy;
- the impossibility of differentiation of osteoporosis degree.
- x-ray computed tomography (RTC);
- magnetic resonance tomography (MRI).
- 1. Women over 65 years old.
- 2. Women under 65 years in postmenopause or premenopause, men aged under 70 years old: low body weight;
- 3. If there are fractures with minimal traumatic effects in history;
- 4. Having diseases or taking medicines that contribute to a reduction in bone mass.
- 5. Men older than 70 years.
- 6. Women with early occurrence of menopause (previously 45 years old).
- 7. Adults with an injury with minimal physical influence.
- 8. All patients having diseases that lead to calcium deficiency.
- 9. Patients of all age groups that are prescribed long-term therapy with glucocorticoid or other drugs that reduce bone mineral density.
- 10. Patients with a diagnosis of osteoporosis to control the effectiveness of treatment.
- 11. Patients with the following risk factors: tendency to falls;
- 12. Lifeline lifestyle;
- 13. Bed regime for more than two months.
- with the cease of reception of hormone-plated drugs;
- women who had a lot of pregnancies and who were breastfied for a long time;
- in the presence of endocrine pathologies (inflammatory diseases of the thyroid gland, Izsenko-Cushing syndrome, testicular failure and decrease in the production of sex hormones in men, diabetes mellitus, pituitary failure or hypothalamus);
- in the presence of pathologies of the gastrointestinal organs (removal of part of the stomach, impaired absorption of trace elements in the intestines, chronic liver diseases);
- in chronic renal failure;
- in blood diseases (myeloma, thalassemia, leukemia, lymphoma);
- with chronic obstructive lung diseases.
- fractures in history;
- long use of anticonvulsants, diuretic products, glucocorticoids;
- muscle mass deficiency with undeveloped skeleton;
- in the presence of chronic pathologies: impaired suction or inflammatory diseases in the intestines, nerve anorexia, systemic red lupus.
- pronounced scoliosis;
- significant vertebral deformation;
- the presence of prostheses in the thigh;
- operations for the combination of bones using metal devices (metallosynthesis);
- fractures;
- pronounced dystrophic diseases of the joints;
- patient weight more than 120 kg;
- growth is greater than 196 cm, in which it is impossible to properly put the subject.
- stop taking calcium preparations for 1 day to survey;
- cook comfortable clothes without metal parts and accessories;
- if a contrast X-ray examination with Barium or CT was held shortly before densitometry, it is necessary to prevent a physician about it, since densitometry is recommended to produce earlier in 10-14 days;
- in women, with suspected pregnancy, the procedure for checking the spine or neck of the femoral bone will also have to cancel (peripheral parts of the body can be examined).
- When studying the lumbar spine - the position on the back. If the patient has brightly expressed lordosis (convex spinal bending in the cervical and lower back), then under the legs there are a special cube, so that they are at an angle of 60-90 degrees to the sequin plane.
- When studying the neck of the femoral bone - the position on the back. The surveyed leg is put so that the central part of the femoral bone was parallel to the middle line of the table, and the foot is rotated inside 15-20 degrees and fixed using a special device. The sole must be perpendicular to the surface of the couch.
- With densitometry of the whole body, which is often held in children, is the position lying on the back. The top point of the head should be 1.5 cc below the scan point. Feet should be together, pressed, and hands - lying along the body.
- When examining the lumbar spine in lateral projection - the position of the patient on the left side. Feet bend in the knees and hip joints. In order for the spine to be parallel to the couch, a special lining is installed under the head and body of the patient. The shoulders should be on the same line and perpendicular to the surface of the couch. The back is fixed with a vertical support and belt.
- In the study of the forearm - the patient is located sitting, and the hand is on the Densitometer table.
- T-Criteria is a comparison with the maximum IPC in a young man of 30 years of the same sex as the examined patient. It is used to evaluate bones in women in period and postmenopausal and men over 50 years old.
- Z-Criteria is a comparison with an average value in the appropriate age group and for this gender. It is used to assess bone tissue in children and adolescents under 20 years old, women before menopause and men under 50 years old.
- in women in premenopause, the bone density is below the norm at the value of Z
- in men under 50 years old, a decrease in the age norm is fixed at z
- in children and adolescents diagnose pathology at z
- inflammatory processes in the spine (spondylitis);
- compression vertebral fractures;
- calcification of blood vessels;
- scoliosis and others.
- MPK \u003d 87 - 113% - norm;
- IPC \u003d 68 - 87% - osteopenia;
Show all
What is a densitometry?
Densitometry (from Latin Densitas - "Density" and Metria - "Measurement") is a group of medical diagnostic methods, allowing to estimate the density of bone skeleton of a human skeleton. To identify the state of the bone system, several types of instrumental examinations are used:
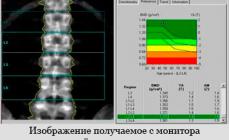
In medical practice, the "Gold Standard" for research is X-ray densitometry or two-energy X-ray absorptiometry. This method of examination allows not only to evaluate the mineral density of bones (IPC), but also to determine the fat and bad-hearted mass of the body. The estimated criterion is the density measured in g / kV. See at the level of 1-4 vertebrae of the lumbar or neck of the femoral bone.
The principle of the survey is the transmission of bones by the X-rays of two energy levels ("soft" and "hard"). They are emitted by an X-ray tube, the dose of the resulting radiation is small - about 1/10 from such under standard chest radigenography. Radiation is absorbed in different ways by the tissues of man. Passing through the body, the rays fall into the detector. A special software calculates the density of bone, fatty and bad tissue (muscles, liquid media). The area of \u200b\u200bthe scanned surface is determined and adjusted by the operator.
Bone X-ray densitometers have high accuracy - their error is not more than 1%. These devices are calibrated using a layout-cast lumbar vertebrae with a known density of the substance from which it is manufactured. Only the qualifications of medical personnel are influenced by the measurement accuracy (correct definition of the survey area) and changing the position of the patient's body.
This method allows you to determine the density of the bones of the axial sections of the skeleton (neck of the thigh, spine) and peripheral departments (wrist, fingers, heels and others). For the last type of research, small mobile densitometers are applied. The one-time dose of radiation obtained by the patient when scanning is small - no more than 0.03 mW, but in Russia to stationary densitometers, the same requirements are presented as radiological cabinets.
For the timely detection of osteoporosis, they conduct a study of the central sections of the skeleton - the lumbar spine and the neck of the thigh. Depending on the configuration at the stationary installation, there may be additional options that allow you to diagnose the forearm, to estimate the deformation or fractures of the vertebrae and determine the composition of the body.
Ultrasound densitometry
With ultrasound densitometry, the measurement of the density of the bone occurs with the help of ultrasound rays. This method is applied to determine common bone losses and with osteoporosis in the initial stage. Most of these devices are designed to evaluate the tissue of the heel bone in women during the period of menopause, since it is this part of the skeleton is subject to metabolic processes to the greatest extent. The density of the bone in the hip neck and in the heel in women almost coincide.
The method of ultrasound densitometry is not so common as X-ray methods of examination, for two reasons:
This method of examination is most often used in the presence of contraindications to radiological methods.

CT and MRI
Computed tomography has one significant advantage compared with previous methods of densitometry - it allows you to get a layered image of bone structures with the subsequent formation of a three-dimensional image. CT refers to additional densitometric technologies. Two types of surveys are used:
The principle of the RCC survey is to pass through the human body of a fan beam of X-rays oriented in the same plane. Passing through dense tissues, the intensity of the rays falls, and it is recorded in special detectors. The density determination of bone tissue is carried out using software based on mathematical integration. After computer analysis, there is a construction of a tomographic image.

Tomography of the neck of the femoral bone
There are 5 generations of tomographic equipment, characterized by the method of interaction of scanning rays and detectors. Tomographs of the 4th generation are of the greatest distribution. The radiation source rotates, and the detectors are located stationary in the circumference and fix the intensity of the rays at each corner of the turn. As a result, you can get a three-dimensional image. Dose of irradiation in the study of the skeleton is 50 st. The advantages of this method are high accuracy (5-10% error), the ability to study any body portion, differentiated assessment of fat, muscular and bone tissue. The disadvantages include the high cost of the survey and the need for its conduct in stationary conditions.
At the heart of MRI (or NMR - nuclear magnetic resonance) lies the ability to orderly orientate the cores of chemical elements under the influence of the magnetic field. Despite its second name (NMR), the method is not related to nuclear physics and safe for humans. The magnetic resonance tomograph consists of a magnet, coils, control processor and display. The equipment varies in the "power" of the magnetic field created - from 0.05 to 4 T. For the densitometry of the bone system, this value must be at least 1.5 T..

MRI of the lumbar spine
MRT allows you to get a cross-sectional image of a person in 20 seconds. The advantage of the method is the lack of X-ray radiation. The disadvantages include the need for manual adjustment of borders of organs and tissues, as well as high-cost examination.

Indications
Densitometry is carried out by the following groups of patients:
In children, bone densitometry of the whole body is carried out with the following risk factors:
With normal bone density values, patients from risk groups are encouraged to undergo a survey at least 1 time in 3 years, and with deviations from the norm - 1 time per year.
Contraindications
MRI-densitometry is not carried out by patients with pacemakers and metal objects implanted into the body. With radiological surveys, the following factors are observed that prevent the scanning of the spine and the femoral bone:
In these cases, they make scanning bones of the forearm. This type of densitometry is also carried out with hyperparathyroidism. Absolute contraindication for X-ray is also pregnancy in women.
Preparation for the examination
To prepare for the procedure for X-ray densitometry, it is necessary to adhere to the following recommendations:
Ultrasound densitometry of special training does not require. Immediately before the procedure, the doctor's assistant enters into a densitometer patient's passport data, indicates the floor, ethnic group, date of birth, growth and weight to compare the results of a survey result with the regulatory data available in the computer's memory.
Conducting densitometry
Depending on the patient's scanning area, it is placed on a densitometer couch in several poses:

Types of research
Scanning procedure lasts from a few seconds to several minutes (usually no longer than 6 minutes.). During ultrasound or x-ray studies, it is necessary to maintain a fixed position. In the survey zone there should be no x-ray-sensitive objects (clasp belts, metallized threads, foil, monetary signs and other). Children conducts a densitometry of the lumbar spine or the whole body excluding the head, as at an early age, calcium is contained in a skull in large quantities. Densitometry is recommended to do on the same apparatus, since different manufacturers of the methodology for analyzing the mineral density of tissue and reference bases are different.

Conducting densitometry
The final conclusion of the survey is made by the doctor, since computer analysis does not take into account individual features: the height of the deformed vertebrae, acquired anatomical changes, the displacement of the research zone, the presence of additional edges or vertebrae, the fight of the vertebrae and others.
Results of surveys
With X-ray densitometry, a quantitative assessment is made using two criteria for the disease:
The unit of measurement is standard deviations of SD (or CO in the Russian-language variant) and the percentage of the norm. For each unit of standard deviation, the risk of osteoporotic fractures increases by 2 times.
The interpretation of the Z-criterion value is carried out as follows:
In modern densitometers, manufacturers already laid the base of regulatory indicators by age and sex for comparison with the data of the patient's surveyed and decrypt results. In pediatrics, an incorrect formulation of the diagnosis of osteoporosis is considered only according to the results of densitometry, since the formation of bone mass ends approximately 25 years. A feature of Z and T criteria is also the fact that with age after 45 years they change slightly, by 13-15%.

Dencilogram of the spine
In men at the age of less than 50 years, the diagnosis is also not installed only on the basis of the measured IPC, other risk factors are also taken into account. As medical research shows, in the elderly men, the value of the IPC, obtained during the densitometry, may not reach the critical level characteristic of osteoporosis. This is due to the physiological characteristics of the male organism - more dense and large bones, lower speed of loss of bone mass. Therefore, for men older than 50 years, if there are fractures, the diagnosis of osteoporosis is established already at T
In some patients, an increase in the value of the IPC is noted. This also testifies to bone pathologies:
With ultrasound densitometry of the heel bone, the estimate is made in% of the maximum mass of bone tissue at 20-30 years. The diagnosis is established on the basis of the following gradation:
The result of a densitometric examination is the conclusion of a doctor. It indicates the diagnosis, numerical values \u200b\u200bof the IPC, the area of \u200b\u200bthe skeleton subjected to irradiation, the type of criterion (T or Z) and the radiation load.
In the mortality structure from non-infectious pathology, the injury occupies the fourth place, after cardiovascular diseases, oncology and diabetes. With age, the risk of spontaneous fractures increases, which is due to the impairment of mineral substances. The bone decreases the level of calcium, which leads to the development of osteoporosis. In addition, in the people of the elderly complications develop much more often due to the slower fusion of fragments. Early diagnosis and prevention of osteoporosis with densitometry becomes especially relevant.
What is the study and its varieties
Densitometry - (from "Densitas" - density) The method of studying a change in the density of bone tissue, which is used by vertebrologists, traumatologists and therapists for the diagnosis and prevention of osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis is a systemic chronic disease, which is characterized by a decrease in bone mass per unit volume.
The study is based on the determination of the mineral composition of bones, and the percentage ratio of calcium compounds. The most often studied individual peripheral departments (radiation or heating bone, hip joint), which reflect the overall condition of the body.
The procedure is carried out with the help of a special apparatus - a densitometer. Depending on the method of obtaining the result, such types of devices distinguish:
- Ultrasonic - portable monoblock apparatus, which studies the rate of passage of ultrasonic wave through bone tissue. The fabric is denser - the easier it will take place and distinct it.
- X-ray absorptiometry is a method that is used most often. The resulting image is represented as an X-ray image with dedicated zones of different density. There are two types: two-photon absorptionity (the entire skeleton is investigated in 2 or more projections), single-photon (to study the density of a certain area).
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- CT scan.
The last two methods are rarely used due to their high cost and duration.
Indications and contraindications to conducting densitometry
Talk about osteoporosis as a pathology of people exclusively elderly - a mistake. States that can cause a decrease in the level of calcium in the blood and, accordingly, the density and strength of the bones are many. The study is recommended in such cases:
- Pathology of parathyroid gland: tumors, hypoparathyroidism (the state of reduced functional activity of the gland with a decrease in the secretion of the parathgamon). This hormone contributes to the absorption of calcium from the intestine and reduces its highlighting by the kidneys.
- Fracture of the bone due to a slight injury in history.
- Reception of drugs that reduce calcium levels: steroid hormones (for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, bronchial asthma), oral contraceptives, loop diuretics (Furosemid, Toramsemid), anticonvulsant (phenobarbital).
- Alcohol abuse.
- Women over 40 years old and men older than 60.
- People over 30 years old, if the relatives have a diagnosis of osteoporosis.
- Persons who lead a low-wear lifestyle.
- Persons who sit on exhausting diets are subject to significant physical exertion.
- For dynamic observation of the patient's condition and control the effectiveness of treatment.
For women, there is a separate list of indications, since the change in the synthesis of estrogen (female hormones) significantly affects the level of calcium in the blood:
- Women in the period of menopause, especially in the case of its early onset (up to 45 years).
- Women who carried out the operation of admexectomy (ovarian removal may be the step of the extirpation of uterine with appendages).
Densitometry - a gentle procedure, therefore there are no absolute contraindications for her. However, due to the use of X-ray irradiation, the method is contraindicated in pregnant and people who are not able to spend 15 minutes in a horizontal position (spine injury).
How to prepare for densitometry
For the maximum objective results of the study, it is necessary:
- During the day to carry out - to stop the reception of drugs containing calcium, including vitamins (Vitrum, Calcinova, etc.).
- If during the last 2 weeks, a study was conducted with contrasting substances (barium sulfate for intestines, angiography, MRI with contrast) - please inform the doctor.
Important! If there is a probability of pregnancy - the doctor should know about it
In addition, it is recommended to wear comfortable and spacious clothes. The procedure lasts about 15 minutes, during which it is impossible to move. When conducting X-ray densitometry, it is necessary to remove all metal objects, because they affect the result.
How does research passes
Densitometry is carried out in a specially equipped diagnostic center. The procedure is painless and safe (dose of X-ray irradiation 400 times less than the fluorography obtained).
The patient, depending on the selected method, is located on the table above which the mobile X-ray apparatus is placed or on a couch next to the ultrasound (ultrasonic study).
When X-ray study, the beam goes from the bottom of the table through the area under study and falls on the registering "sleeve", located above the patient. The resulting shot is transmitted to the monitor screen, where analysis is performed using a special computer program. The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes.
Ultrasound densitometry implies the use of special sensors that are put on the heel or finger of the patient. Within 3-5 minutes, the passage of ultrasonic wave through bone tissue is carried out.
Advantage of research and possible complications
Before the appearance of densitometry, the only way to diagnose changes in bone tissue was x-ray. However, the informativeness of densitometry is an order of magnitude higher than that of an ordinary X-ray.
The table shows a comparison of the ultrasonic version of the study and radiography.
|
Criterion |
Ultrasound densitometry |
Radiography |
|
Method of obtaining an image |
Bone Ultrasound Wave Movement |
Dispersion of the radiation beam in the tissues of different density with the greatest accumulation in the bones |
|
Visualization of other structures |
Held |
Only bone fabrics |
|
Quantitative: the degree of reduction in bone density is determined |
Qualitative: the presence of changes |
|
|
Diagnosis of osteoporosis |
In the early stages |
In pronounced stages with a loss of at least 30% density |
|
Duration |
||
|
Safety |
Safe study |
X-ray irradiation |
X-ray data allow you to diagnose osteoporosis at the stages when the treatment is ineffective. This method is used to diagnose complications, for example, a vertebral body fracture.
The lack of possible complications after the study is another important advantage of densitometry.
How to decipher the results of densitometry

Analysis of the data obtained during the study is carried out in three main indicators:
- Tissue density expressed in g / cm2.
- T-indicator (hypothetical research statistics). Determined by comparing the resulting density result with a bone density indicator in a woman aged 30 years.
- Z-indicator (standardized). Comparison of the result obtained with the result of a healthy person of the same age and gender.
For the T- and Z indicator there is a single estimate scale, presented in Table:
Doctors recommend to conduct a study every 2 years for people with testimony with the aim of early diagnosis of changes and began preventive treatment of osteoporosis. This method allows you to quickly, painlessly and effectively diagnose changes and prevent possible fractures in the future.
The video presents x-ray two-photon absorptiometry.