Crossword on biology for grade 8 "Fish"
Crossword for checking knowledge on "Fish"
Shchptsova Natalia Borisovna. Biology teacher GBOU "Plogoshskaya special boarding school"Toropetsky district, Tver region.Description of the material: The submitted crossword is designed to check the knowledge of biology on the theme of "fish" in the 8th grade of the Correction School of VIII of the species. Also, it can be used in primary grades and in extracurricular work on the subject. Crossword will be interesting to teachers, educators and parents.
Purpose: Check the knowledge gained about fish.
Tasks:
consolidate knowledge on the topic "Fish";
develop memory, creative activity, interest in the subject;
Rise curiosity, expand the horizons, educate love for wildlife.
Questions:
Vertically:
2. Fresh mining.
3. It turns into a fish larva.
5. With them, fish swims.
8. Great nemid.
10. Wild ancestor Carp.
11. Marine fishing fish.
12. She covered the body of fish.
13. Fish eggs.
Horizontally:
1. Fish, building a nest.
4. Fishing breeding.
6. Large fish cluster.
7. Fish respiratory body.
9. Large predatory river fish.
14. Aquarium fishwhich gives rise to living fry.
15. Domesticated fish derived by man.



Used Books:
1.A.I. Nikishov, biology 8 class. Animals. Textbook.
2.A.I. Nikashov Biology 8 class Animals. Workbook.
Crossword "Biology Development History" 1.Russian scientist proven that the development of all organisms begins with an egg, and in the early stages of development, similarities are found in the structure of animal germs relating to different classes. 2. Suggesting the ship, on which Ch. Darvin went to the world journey. 3. School scientist, who was the basis of his classification laid the principle of hierarchy (coodus) of taxa. 4.Galian scientist who created the theory of speciation. 5. The works of which throughout the Middle Ages were the basis of wildlife ideas. 6. Scientific, opened cell theory. 7. Scientific, whose theory has had a great influence on the worldview of Ch. D Darvina. 8. Processes of the historical development of wildlife since the emergence of life on Earth to modernity. 9. Double nomenclature. Crossword "The main properties of living organisms"
Horizontally 1. The substance of all biocenoses of the planet, in which the cycle of substances and the conversion of the energy associated with the vital activity of all living organisms living on Earth are occurring. 2. Individual development of the body. 3. Delicacy of living matter to reproduce themselves like. 4. The capacity of the organisms of different types of 5.-in-law bodies that exist on Earth, which are open self-regulating and self-reproduced systems built from polymers 6. The proper single-cell organisms capable of performing all the functions necessary to ensure their livelihoods 7. Ensure and directional development of wildlife, accompanied by the formation of new species and progressive complication of life forms
8. Enecessible, directed natural change in facilities of living and inanimate nature 9. Assumption of organisms of different types and environmental factors of their habitat, combined metabolism and energy into a single natural vertical complex 10. Historical development of the body 11. Organism, which is a holistic system of organs, 12.And the body capable of independent existence to acquire new features and properties to the conditions of existence in specific natural conditions 13. The equipment of the organisms to transmit their signs and properties and features of development from generation to generation 14. The capacity of the organisms of the same species uniting the common place Habitat Crossword "Development of Biology in the Dalvinvinsky period" with answers without answers 1.Franzuz natural scientist creating the first evolutionary theory and proposed term "biology". Laid the basics natural System Classification.
2.Theorey, which put the end of the disputes of adherents of the immutability of species and natural evolutionists. 3.I. modern science The highest taxon was ... 4. A large taxon in Linnei's system. 5. Principle "Sophillary". 6.Rorbor created in the 17th century and used in biological studies. 7. The Greek "Location is fine." 8.Teoria is responsible for the occurrence of complex organisms, their adaptive signs, a variety of organic peace and its preservation in nature and other issues. 9. Schveda naturalist described more than 8000 species of plants, which established uniform terminology and the procedure for describing species. 10. "Double" nomenclature. 11.Peregreic philosopher describing more than 500 species of various plants and animals. 12. The susceptibility of individuals with the ability to crossbage with the formation of the fruit offspring living in a particular territory. 13.Galian natural resource - the creator of the modern theory of evolution. Crossword "Building and Cage Functions Horizontal
1. The arranged organisms whose cells are adapted to oxygen consumption. 2. Theores, which preserved the features of the deepest antiquity to the present days of the simplicity of the structure. 3. Energy stations of cells. 4. The organizes having a separate kernel in the cell. Vertical 5. Durable animal cell structures that are responsible for performing a function or another. 6.Beaner organisms. Crossword "Prokaryotic cell" horizontally 1. The process of deploying a part of the cytoplasm from the maternal cell. 2. Wrestling molecule containing hereditary information having a rings in the cytoplasm of a bacterial cell. 3. Education in the bacterial cell separating the cytoplasm from the cell wall. 4. Formal method of breeding bacteria. Vertically 5. Bandal cells of spherical shape. 6. Investments in the cytoplasm of a bacterial cell, in which protein synthesis occurs. 7. Bacterial cells of a winding form.
8. Bacterial cells elongated form. 9. The extensions are inside a bacterial cell that can extend her life in the absence of external energy sources. 10.Organoid, absent in the bacterial cell. Crossword "Eukaryotic cell. The cytoplasm "horizontally 1. The network formed by a complex membrane system that permeates the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells. 2. Process capture of solid particles of the membrane of the cell. 3. Processes of the capture of the intercellular fluid of the membrane cell. 4. Power on the plant cell. 5.Mogenous smallest holes available in the cytoplasmic membrane.
6.Spherical calves consisting of subunits. 7.RNA Synthesizing in the kernel on the DNA molecule of one of the chromosomes. 8. The color plasts of the plant cell, in which starch is synthesized from monosaccharides and disaccharides. 9.Plastides, including various pigments, from group of carotenoids, giving a bright color of colors and fruits. 10. The cages having spherical, oval, cylindrical, filamentous and other forms whose function is to form ATP. 11. The various substances that are in the cytoplasm of cells that have a property that occurs, then disappear in the process of its livelihoods. 12. Developed system in a vegetable cell that causes its osmotic properties. 13.seen plasts containing chlorophyll pigment. Vertically 14.Organoids of the plant cell in which the primary synthesis of organic substances from inorganic due to the energy of light occurs. 15.Anapressed state of the cell wall. 16. Value of the cell membrane. 17. Pricing the structure of the block organization of the cell. 18.Vide EPS, the function of which protein synthesis. 19.Vide EPS, where the synthesis of lipids and carbohydrates occurs. 20. Next oval calves filled with digestive enzymes.
View the contents of the document
"Crossword"
Horizontally
1. Based in potato tubers (leukoplasts)
7. Chromosoma collection characteristic of one type (karyotype)
8. In their cells there is a kernel (eukaryota
10.Things in the kernel, the RNA synthesizes (nuclei)
11.Bacteria and blue-green algae (prokaryotes)
12.Is them consists of a cell center (centrioli)
14. Processing of the seizure of food particles (phagocytosis)
16. Bandatory component of any cell (shell)
17. In their synthesis of ATP (mitochondria)
19. Consider photosynthesis (chlorophyll)
20. Fill the digestive function (lysosomes)
Vertically
2. There are plants and fungi (vacuole)
3. Mitochondria internal membrane stacks (Crysta)
4. Process of the absorption of water droplets (Pinocytosis)
5. Increased semi-finished cell medium (cytoplasm)
6. In autumn, chloroplasts are converted (chromoplasts)
9. The main component of the eukaryotic cell (kernel)
13. Processing the outgoing cells of cell metabolism (exocytosis)
15.To in the composition of the leaves, stems (chloroplasts)
18.Shemable small non-smiled organoid cell (ribosome)
View the contents of the presentation
"Crossword Cage Build"









Start of form
End of form
1. All changes occurring in nature.
2. Nature to which such objects include plants, mushrooms, animals, man.
3. The source of heat and light for everything alive on earth.
4. The phenomena of nature associated with the change in the seasons of the year.
5. Nature to which such objects include: sun, stars, air, water, stones.
6. Device for measuring temperature.
Start of form
End of form

1. Deficuous shrub.
2. Plants that have leaves in the form of plates.
3. Plants that have one thick stem from the root.
4. Thick stalk at the tree.
5. Coniferous shrub.
6. Plants. which leaves in the form of needles.
7. Leaves of coniferous trees.
8. Herbatous plants that have soft and juicy stalks.
Start of form
End of form

1. The group of animals to which the snakes belong, lizards, turtles, crocodiles.
2. Animals whose body is covered with wool and feed cubs with cubs.
3. Animals with six legs.
4. A group of animals to which the frogs and toad are.
5. Animals whose body is covered with feathers.
7. Beasts or ...
Start of form
End of form

1. Snowfall with strong wind.
2. The time of year, when the sun rises in the sky low, and the days are short.
3. Fluffy snow fruit on trees.
4. Winter phenomenon in inanimate natureWhen the snow is tapping, becomes wet and easy to do.
5. Snow that falling to the ground in the windless days calmly, slowly.
Start of form
End of form

1. Internal human body. It distinguishes acidic juice capable of digesting most of the food.
2. Helps to digest food in the intestine.
3. Part of the human body.
4. It is almost eight meters long.
5. Lower limb.
6. Upper limb.
7. Internal human body. Tight muscular bag.
Start of form
End of form

1. The border of the horizon, where the sky seems to be with the earth's surface.
2. Ground surfacewhich we see around ourselves.
3. The closest environment of a person.
4. Family history in several generations.
5. The device for determining the side of the horizon.
6. One of the main sides of the horizon.
Start of form
End of form

1. Low places on the plains.
2. Color denoting on the lowlands map.
3. Wide spill of the river from the shores.
4. The time of year when the sun rises in the sky highly, and the days become longer.
5. High places on the plains.
6. Color denoting on highway map.
7. Spring phenomenonWhen the ice floes, the river, large and small, quickly float over the flow, facing and breaking.
8. What is denoted on geographic map Green and yellow color?
9. What is indicated on a geographical map blue?
10. What is indicated on the geographic map brown?
Start of form
End of form
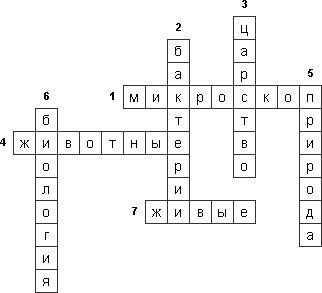
1. Magnifying device.
2. Tiny organisms.
3. Large group of living organisms.
4. One of the kingdoms of wildlife.
5. The most important condition Human life.
6. Science studying live nature.
7. Beings that breathe, grow, eat, develop, bring offspring.
Start of form
End of form

1. Head of the monarchist state.
2. One of the symbols of the state.
3. One of the symbols of the state.
4. Official language in Russia.
5. They are depicted on the political map of the world.
6. Head of the Russian state.
7. Part of society to which you belong.
8. Human society.
9. Man of any state.
10. Little part of society.
11. One of the symbols of the state.
Start of form
End of form

1. Gas, which is distinguished from the body living beings.
2. Air does not spend the air ...
3. Air when heated ...
4. One of the properties of air.
5. Air when cooled ...
6. Gas, which absorb living beings from the air.
7. Fresh air it does not have.
8. One of the properties of air.
9. Gas mixture.
Start of form
End of form

1. High above the ground they are formed from droplets and ice floes.
2. The process when water evaporates from the surface of the earth, forms clouds, then in the form of rain or snow returns to Earth.
3. Water in solid state.
4. Water condition in the form of steam.
5. The substance that is part of any organism.
Start of form
End of form

1. Russian scientist creating soil science.
2. It gives the soil dark color.
3. Nutrients, without which plants can not live.
4. In the soil it is also there.
5. Science of soils.
6. They are also solid bodies.
7. The main property of the soil.
8. Upper fertile layer of land.
9. Salt remaining on the glass after evaporation of water.
10. One of the gaseous substances contained in the soil.
Start of form
End of form

1. Plants that have flowers and fruits.
2. Plants - residents of water.
3. Science of plants.
4. Plants that, instead of leaves - CHINA.
5. Grows on wet places. It has stalks and leaves, but he does not have roots, flowers and fruits with seeds.
6. It is easy to learn about the beautiful leaves, similar to big feathers. There are roots and stems, but there is no flowers, fruits and seeds.
7. Green "clothes" of land.
Start of form
End of form

1. Animals whose body is covered with dry scales, and some also have a shell.
2. Animals whose body is covered with feathers.
3. Animals whose body is covered with wool. They feed their children with milk.
4. A group of animals that have six legs.
5. Animals whose skin is naked, gentle. Part of life they spend on land, and part in the water, for which they received their name.
6. Water animals whose body is covered with scales.
Start of form
End of form

1. Animals that eat insects.
2. Animals that eat animal, and vegetable food.
3. These "chains" begin with plants.
4. Herp is a wonderful defense - ...
5. Insects who eat other insects.
6. The hare is fast ...
7. Pets feeding on vegetable food.
Start of form
End of form

1. An adult appears from the doll ...
2. Fixed caterpillar.
3. Egg fish.
4. Butterfly larvae urticaria.
5. These insects have no dolls.
Start of form
End of form

1 deadly poisonous mushroom.
2. The visible part of the mushroom in the forest.
3. An amazing organism consisting of fungus and algae.
4. Underground part of the mushroom.
5. Visible part of the fungus in the forest.
Start of form
End of form

1. Touch body.
2. Human ability to feel smells.
3. The sense of smell.
4. Vision body.
5. Taste.
6. Organ hearing.
Start of form
End of form

1. There are many of them in vegetables and fruits.
2. Substances that serve as the main "building material" for the human body.
3. They provide the body with energy, and also serve as a "building material" of the body.
4. Main energy supplier for our body.
Start of form
End of form

1. Heavenly bodies rotating around the sun.
2. How in antiquity called astronomers?
3. An immense space with stars, planets and other celestial bodies.
4. Name of our planet.
5. Science of heavenly or cosmic bodies.
6. The star around which ten planets rotate, among which our planet.
Start of form
End of form

1. Natural satellite land.
2. The first planet from the sun.
3. The planet called the name of the sea king.
4. Planet, having 30 satellites and well-noticeable rings consisting of stones and blocks rotating around it.
5. Planet, with two satellites.
6. Second planet from the sun.
7. Planet having one natural satellite.
Start of form
End of form

1. Nightly predatory bird listed in the Red Book of Russia.
2. Mixed wood tree.
3. "Light Our Planet."
4. illegal animal shooting.
5. Mixed forest tree.
6. A plant growing in the Far East, listed in the Red Book of Russia.
7. Variety coniferous forestwhere pines are mainly growing.
8. The famous beast of the reserve located in the south of the Moscow region, on the banks of the Oka.
9. These special substances allocate the leaves of many trees, from which pathogenic bacteria dying.
10. Black spot remaining after the fire in the forest and does not grab the grass for many years.
11. Large forest animal.
12. What can happen if you leave glass jars, bottles in the forest?
Start of form
End of form

1. Predatory insect, whose mining flies.
2. Rare large beetle hiding under the stones.
3. Large animal living in the forests.
4. Bird living on the seashore feeding fish.
5. Amazing beauty butterfly.
6. The inhabitant of the sea, burning human as strap.
7. Loudly shocking insect, powered by plant juice.
8. Skyfish, body shape resembles a sewing needle.
9. Sea bird feeding fish.
Start of form
End of form

1. Water vaults on Earth, which is so necessary to all alive.
2. Natural reservoir planet.
3. Artificial water.
4. Natural reservoir.
5. Huge natural reservoir on earth.
6. Artificial water.
Start of form
End of form

1. Mineral consisting of a field sword, quartz and mica animal.
2. Special variety of limestone. They write to them school boardFrom it makes a tooth powder.
3. Durable white or gray stone formed from alive beings. From it get lime.
4. The clay property is good and retaining the shape that she is given.
5. Widespalled rock formation formed in the destruction of granite.
6. The main property of granite.
7. Important property of peat.
8. The car operating in the career.
9. It is used to prepare for construction solutions.
10. Products from burned clay.
11. Mineral, dark brownconsisting of plants residue, loose, continuing, lighter than water.
Start of form
End of form

1. From all sides, the dragonment of these insects is coming to the meadow.
2. Nature community.
3. Beetles, collecting animal litters in their mink, thereby popping for themselves and larvae.
4. Not bright grass growing in the meadow.
5. Insect feeding nectar flowers.
6. Insect pollinator.
7. Insect-sanitary, bursting into the soil of dead birds and animals.
8. Meadow plant.
9. The inflorescence of this meadow herba resembles lisus tail.
Start of form
End of form

1.Gribes growing in the meadow.
2. This bird constantly shakes the tail, for which he received its name.
3. Meadow bird running around the ground.
4. Amphibious insects fed.
5. For them from the forest, owls on the meadow arrive.
6. This bird is also called Dergach.
7. Large predatory bird arriving on the meadow in search of food.
8. Presbyer, which serves insects.
Start of form
End of form

1. The roots of this plant are attached to the bottom, and the wide leaves float on the surface of the reservoir.
2. In the thickness of the water flooded vegetable larvae frogs and toads.
3. Microscopic green plants.
4. Predatory beetle.
5. Fish feeding by plants, insect larvae.
6. Predatory Fish reservoir.
7. The roots of this plant are attached to the bottom, and the wide leaves float on the surface of the reservoir.
8. Predatory bug, rapidly running over the surface of the water.
9. Plant floating on the surface of the water.
Start of form
End of form

1. The mammal living in the reservoir.
2. Mollusks living at the bottom of the reservoir.
3. A mammal having a valuable fur living in a reservoir.
4. Mollusk sash.
5. The roots of this plant are attached to the bottom, and the stalks and leaves rise above the water of the reservoir.
6. The roots of this plant are attached to the bottom, and the stalks and leaves rise above the water of the reservoir.
7. Herbivinal snail.
8. The roots of this plant are attached to the bottom, and the stems and leaves rise above the water of the reservoir.
9. Mammal living near the water.
10. Waterfowl Bird.
Start of form
End of form

1. In the southern regions of our country, this grain culture is grown by grain, and in more northern regions - silage is obtained from it.
2. From the flour of this culture, rusty bread bake.
3. Field culture, from which sunflower oil is obtained.
4. Moody - this is when they grow ... culture.
5. From the tubers of this field culture get starch.
6. Green mass from corn.
7. Grain culture from which millet gets.
8. Grain culture from which a buckwheat croup is obtained.
9. From this field culture, fiber is obtained for the manufacture of tissues.
10. Main field crops.
11. The grain culture from which the pearl cereal is obtained.
12. The main grain culture of our country.
13. Oatmeal is made of these grains.
14. Field culture.
Start of form
End of form

1. The branch of crop production by growing vegetable crops.
2. Vegetable culture rich in vitamins.
3. Substances are contained in Luke, garlic of which the pathogenic bacteria is killed.
4. Vegetable culture.
5. Vegetable culture is rich in vitamin "Growth".
6. Vegetable culture with a sharp smell.
7. Heat-loving vegetable culture containing a large number of (up to 90%) water.
Start of form
End of form

1. Widespread fruit culture.
2. Barbed fruit culture.
3. This fruit tree Fruit has a blue color.
4. Sweet berry.
5. The fruit of this tree resembles the form of a light bulb.
Start of form
End of form

1. The branch of crops engaged in the cultivation of field crops.
2. The plant industry engaged in the cultivation of fruit crops.
3. The branch of crop production is growing of vegetable crops.
4. Farm industry engaged in growing floral crops.
Start of form
End of form

1. The branch of animal husbandry engaged in growing and breeding pigs.
2. Livestock industry engaged in the cultivation and breeding of home rabbits.
3. Branch of animal husbandry engaged in the cultivation and breeding of horses.
4. Livestock industry engaged in growing and breeding domestic birds.
5. A branch of animal husbandry engaged in the cultivation and breeding of bees.
Start of form
End of form

1. The most important property of iron ore is.
2. Small pressed peat lumps used as fuel, fertilizer.
3. Variety of coal.
4. Main raw materials for mechanical engineering.
5. Get coal in quarries and ....
6. Ore having a common name and containing valuable metals, such as vanadium, titanium, cobalt.
7. Best grades Stone coal, shiny, black.
8. Fragile iron alloy with carbon.
9. Variety of coal.
10. Mountain breed formed in the depths of the Earth from the remains of ancient plants.
Start of form
End of form

1. For oil production, you need deep ....
2. For oil mining build ... tower.
3. Thick oil liquid with a sharp smell formed from plants and animal residue, which lived a lot of millions of years ago.
4. Colorless light gas, resulting from plants and animals, which once lived on the planet.
5. The valuable metal contained in iron Rud.without which it is not necessary when creating space missiles.
6. Export of goods abroad for their sale.
7. Liquid fuel For cars.
Start of form
End of form

1. A tier located under the trees.
2. Community of all forest inhabitants are closely related to each other.
3. Plants forming the highest tier.
4. Tier, where MAs and lichens grow.
5. Many forest animals feed them.
6. Mushroom, which is treated by elk.
7. Below the shrubs grow ....
8. Tier, below the tier of shrubs.
9. Mushrooms contribute ... plant residues in the forest.
10. "Floors" in the forest.
Start of form
End of form

1. Meteor that has reached the surface of the Earth.
2. Small planets.
3. Planet moving along the closest to the sun orbit.
4. Translated from the ancient Greek means "wandering".
5. "Vladyka Food, Father and Mother of People." Who spoke about the Egyptians?
6. Planet for Saturn.
7. "Falling Stars."
8. Big systemwhich includes millions and millions of stars.
9. Heavenly body consisting of solid particles and gas clots. It has tail awarded towards the sun.
10. The second from the sun planet.
11. Planet rotating in the fourth orbit from the sun.
12. Planet with gigantic rings consisting of stones and ice.
Start of form
End of form

1. When moving from a liquid state in solid, water is its volume ...
2. Transmission of heat from a heated body part to another, less heated.
3. The most unusual substance on Earth.
4. Natural disaster, during which water demoloses bridges, destroys the shores and buildings, destroys crops, takes human life.
5. Water shell of the Earth.
6. Underground emptiness.
7. Gaseous water condition.
8. Liquid containing foreign substances that are evenly distributed in it.
9. The smallest droplets of water formed in the air.
10. The solid state of the water.
11. Unattended different particles that make water muddy.
Start of form
End of form

1. Plants growing in themselves in nature.
2. Green Pigment Plants.
3. The organ of seed reproduction.
4. The oldest profession of a person who was engaged in the cultivation of plants for himself.
5. Organic substance formed in the process of photosynthesis in plants.
6. The formation of organic substances from inorganic in plants leaves.
7. Shadowish flowering plant.
8. Plants that man specially grows to use in everyday life.
9. The coloring agent accumulating in the tissues and organs of the plant.
10. Stem with leaves and kidneys located on it.
11. The result of plants of the past years.
Start of form
End of form

1. Stem with leaves and kidneys located on it.
2. Flowering plant organ.
3. It ripens pollen.
4. The organ of seed reproduction in flowering plants.
5. The above-ground organ of the flower plant, the function of which to take leaves to the light and carry out water with mineral salts throughout the plant.
6. All flower petals together.
7. Fruit is formed from it.
8. The underground organ of the flowering plant.
9. The special organ of the flowering plant, where the formation of organic substances from inorganic.
10. It is inside the fetus.
Start of form
End of form

1. Unicellular mushrooms used by man in bread maker and winemaking.
2. It has a different color and shape in mushrooms.
3. Imperceptible, invisible mushrooms.
4. Edible mushroom living under an aspen.
5. The body of the mushroom.
6. Edible lamellar mushroom.
7. Edible Hat Mushroom.
8. Special group living beings, which does not apply to any plants or animals.
9. The body of the mushroom, which people put in a basket.
10. Mushroom that is in the trees and the destroyer of their wood.
11. Hat mushroom.
12. Edible mushrooms.
13. Edible mushrooms, similar to freight.
Start of form
End of form

1. Bread culture.
2. Annual or perennial cultures, juicy fleshy parts of which man eats in food.
3. A group of plants cultivating by man to obtain fruits, berries, nuts.
4. Cultural plant, whose homeland is a European-Siberian center.
5. Plants giving raw materials for various sectors of the national economy.
6. Vegetable, whose homeland Mexico.
7. The most important group of cultivated plants cultivated mainly to obtain grain.
8. Grain Culture, Motherland of which South India.
9. Her homeland is China.
10. "Sunny Flower". For a long time in Russia remained decorative.
11. Cultures from which vegetable oil is obtained.
12. Plant from Mexico.
14. This vegetable is genital from the Mediterranean and Central Asia
Start of form
End of form

1. Animals feed on only vegetation.
2. Animals whose life is completely dependent on the conditions ambient.
3. Unlock animal inhabiting in the forest.
4. Mammal in Figure 105.
5. Animals whose life is completely dependent on humans.
6. Reptiles in Figure 105.
7. Animals that feed exclusively by other animals.
8. Animals eating only insects.
9. Animals, eating and plants, and other animals.
10. A large predator in Figure 105.
11. A special substance that gives the vegetable cell hardness and a constant form.
12. Bird in Figure 105.
Start of form
End of form

Horizontally
1. Education of the upper and lower jaws.
2. The vertebrae that completely agrees with each other with iliac bones.
3. Mass of breast muscles.
4. Bottom of legs.
5. Muscles raising wing.
6. Skin iron in birds.
7. Fitting belt formed by three pair bones: Voronena, blades, clavicle.
8. Belt of the hind limbs.
Vertically
9. Type of contour pen pen.
10. Place of attachment of tail feathers.
11. Feathers forming the basis of plumage.
12. Outdoor Pokrov birds.
13. The number of sacral vertebrae in birds.
14. Regular process of replacing feathers in birds.
15. Animals whose forelimbs are converted into wings.
Start of form
End of form

1. Musculatory faces are especially developed at the instrument of primates.
2. The name of the limbs in the bats.
3. Breast and abdominal departments.
4. Hair change in some mammals occurring in spring and autumn.
5. Big finger in mammals ... four remaining fingers.
6. Pokrov mammals.
7. The limb in high-speed animals is represented ...
8. The ancestors of the ancient mammals.
9. Segmented bone plate in mammalian skeleton.
10. The limb of floating mammals performing the function of movement in the thickness of water.
11. A constant number of cervical vertebrae in mammals.
12. The skeleton department consisting of four thorough vertebrae.
13. The domed muscle, the function of which consists in changing the volume of the chest cavity when the animal breathing.
14. The most highly organized class of vertebrate animals.
15. Outer skin.
16. Primate detachment finite type.
17. The basis of the mammalian shoulder belt.
18. Very long rigid hair performing a tactile function.
Start of form
End of form

1. The construction is similar to sponges, but they already have a digestive cavity, cell differentiation is observed (separation by functions)
2. These animals consist of three departments: head, chest, abdomen. On the head there is one pair of complex eyes, simple eyes, mustaches, oral appendages. The chest carries three pairs of walking feet, wings. Fucking breathing.
3. Highly organized warm-blooded animals. The skin has hair cover and numerous skin glands. The heart is four-chamber. The brain is well developed; There is a big hemisphey bark. Young feed milk.
4.Conally water animals having a streamlined body. Breath gill. The heart is two-chamber. The limbs have the shape of the fins.
5. Tyi worms have a spindle-shaped body shape, internal organs are located in the body cavity.
6.This marine animals, predominantly bottom, having radial symmetry of the body. The skeleton is formed by lime plates. Characteristic feature - Water affirmation.
7.The main aquatic animals. Breatha with habies. The body consists of heads, chest (or pumped) and abdomen. The headband carries five pairs of walking feet. Eyes are complex.
8. And the body consists of heads, torso and legs and, as a rule, concluded in the sink. There is a skin fold - mantle.
10.This inhabitants of our planet there are 1.5-2 million species. It is characterized by a heterotrophic type of food, active metabolism, mobility, limited growth.
11. Highly organized warm-blooded animals. Most of them are able to fly. The skin is almost deprived of the skin glands. The body is covered with feathers. The heart is four-chamber.
12.This type combines animals having segmental limbs and solid bodies of the body.
13.In the main inhabitants of the sushi. Breathing pulmonary, dry skin. There are two circles of blood circulation, three-chamber heart.
14. Sushi clothers. The body of these animals consists of two departments. There are four pairs of walking extremities. Eyes simple. A mustache is absent. Breathe with pulmonary bags and trachemetes.
15. Life, whose body consists of one cell. They have microscopic sizes, many have special purpose organides.
16.Conibly aquatic animals. Their body resembles a bag, permeated by pore; It is formed by two layers of cells. There are no organs and fabrics.
17. High, having a sealing body, every segment on the sides has bristles that help them move. Blood system is closed. In the head office there are inspiration and satellite nerve nodes.
18. This is in water, and on land. Skin wet. Adult individuals breathe lungs and skin. Three-chamber heart. The development of larvae occurs in water.
Start of form
End of form

1. They are going to flocks and are very harmful to agriculture, for which they got the name "execution of Egypt".
2. Day predatory insect, feeds by mosquitoes and other small insects. Large head with big painful eyes. The larvae attack the headastrics and fry fish.
3. Education on the adolescence of females, to lay eggs to the ground, on the surface of plants or inside the body.
4. Domestic view of the insect.
5. The biggest detachment of insects.
6. Representative of rectal.
8. Public insect.
9. Beetle, performing the function of the sanitary, burling the manure into the soil.
10. Mostly a night animal, not carrying cold inhabitants in human housing.
11. Eggs of lice.
12. Class, whose animals were called for characteristic notches on the trouser.
13. Straight.
14. They are distributed throughout ground Shar.. Adults do not eat, live one or a few days.
15. Animals of this class are black, straw-fawn, brownish color. Their shooting occurs, as in the grasshoppers.
16. These animals lead an underground lifestyle. The front limbs are designed for digging. Harm garden plants, damaging the root system.
17. Beetle, harms fish farming, as its larvae attack fry fish.
18. "Dwarte".
Start of form
End of form

1. An amazing engineering plant from wax consisting of hexagon cells located in two layers, with an entrance facing opposite sides.
2. Domestone interflower public insect.
3. Bee. Barren female.
4. Cool insects transmitting dangerous diseases to man.
5. The detachment, the front wings of representatives half consist of solid chitin, and the other part of the wings - is confused and has a housing.
6. Butterfly, flying away in the autumn in the southern countries of Africa, in India or Iran.
7. Painful, harming agriculture.
8. Refluenced.
9. Butterfly larva.
10. Sequential chain of congenital responses to various stimuli.
11. Insect detachment, which have well-developed front wings.
12. Bee, latching eggs.
13. Water bugs.
14. Domination of the butterfly.
15. Insects whose wings are covered with scales.
16. Bee glue.
17. Butterfly, which flies alone in warm edges.
18. Male in the ulle.
19. The bloodstream.
Start of form
End of form

1. Complete or partial disruption of bone integrity.
2. The injury associated with the outlet of the bone head is not completely.
3. Fracture when skin covers and muscles are not violated.
4. Damage to the tissues and organs without disrupting the integrity of the skin.
5. Fracture when skin covers and muscles are violated.
6. Special medical plank for fixing immobility of the injured body part.
7. Resistant shift of the joint bones, in which the head of one bone comes out of the articular fox.
Start of form
End of form

1. The beginning of blood circulation is considered ...
2. Long bubbles.
4. Number of human heart chambers.
5. Artery, a swinging heart in the form of a crown.
6. Circulation circle, starting in the left ventricle.
7. An unlocked system in the human body, which allows to purify intercellular gaps from unnecessary substances.
8. Blood entering the right ventricle.
9. Part of the heart, containing rich oxygen arterial blood.
10. Part of the heart, containing venous blood carbonated gas.
11. They supply blood all organs and fabrics.
Start of form
End of form

1. Education on the skin, as a result of the blockage of brood ducts.
2. Damage to the skin caused by chemical or thermal stimuli.
3. Disease caused by scabies itch.
4. Cracks in the corners of the mouth, caused by the lack of vitamin "B 2 ».
5. The bandage that is necessary to make the victim with strong frostbite.
6. Disorders of the condition of the skin associated with the endocrine system.
7. Skin supercooling, manifested by the penetration of skin.
8. Damage to the skin surface.
9. One of the common fungal skin diseases.
10. Skin disease associated with vitamin disadvantages.
11. Type of skin, with excess nutrition.
Start of form
End of form

1. The brain department, where there are centers that ensure the clarity of view and hearing.
2. The brain, which includes an oblong brain, cerebellum, bridge, middle brain, intermediate and large brain hemispheres.
3. The brain consisting of three parts is the top, central and lower.
4. The brain, in its structure and functions, is similar to the spinal cord.
5. Lower part of the intermediate brain.
6. Speakers of the surface of large hemispheres.
7. It coordinates movement, makes them smooth, accurate.
8. Division N.S., managing internal organs, smooth muscles and metabolism.
9. Central part of the intermediate brain.
10. The nervous system department specializing in the perception of information coming from the environment and managing body movements in space.
11. The highest body of the autonomous nervous system.
12. Zone located ahead of the central furrow.
13. Digitations on the surface of the hemispheres.
14. Nervous systemregulating the work of the cross-striped muscular fabric of skeletal muscles.
15. An auditory paths pass through it.
Start of form
End of form

1. The presented human body is capable of perceiving and processing a large amount of information.
2. The surface layer of cerebellum hemispheres.
3.Well + bridge + medium + intermediate \u003d?
4. It is located where nerve fibers are located, and there are centers associated with facial expressions, chewing functions.
5. Mind, responsible for vital centers involved in the regulation of breathing, heart activities, vessels.
6. Mind, conducting impulses to the crust of large hemispheres from the skin receptors, the senses, the centers of thirst, hunger, maintain the constancy of the inner environment of the body, etc.
7. A brain that participates in the coordination of accurate, targeted movements.
8. The most small brain department is involved in the reflex regulation of various kinds of movements, which occur under the influence of visual and hearing impulses.
9. Mind, located in the skull cavity and having a complicated form.
Start of form
End of form

1.Mannively important man.
2. The restned, middle part of the short bone.
3. Costor tubular bone.
4. Perhaps having a complex shape and consisting of several parts having a different structure and outlines.
5. Involved short bone ends.
6. One of the skeleton parts.
7. The source function of the skeleton.
8. It consists of more than 200 bones connected.
9.Alit bone.
10.Samed bone.
11. The most large and long bone in the skeleton of man.
12. Perhaps participating in the formation of walls of cavities containing internal organs.
13. Dentile tube bone of the upper limb person.
14.Tright bone body is available ...
15.Alit bone.
16. The skeleton forming the product for vital organs of the human genitourinary system.
Start of form
End of form

1. Paired, the largest bones of the facial department.
2. Unpaired brain department.
3. Lower moving part of the skull.
4. One of the unpaired bones of the brain department of the skull.
5. One of the paired largest bones of the facial department.
6. Paired bones of the brain department of the skull.
7. One of the skull departments.
8. Paired brain departments.
9. Skull department.
10. Paired bones of the facial department.
11. Paired bones of the facial department.
12. Bone located on the neck.
13. Skull.
Start of form
End of form

1. The spine department consisting of five vertebrae
2. The spine department formed from 4-5 vertebrae
3. The spine department consisting of seven vertebrae
4. Part of the vertebra
5. Spinal Department, head
6. The Spinal Department following the lumbar
7. Part of the vertebra
8. Part of the vertebra
9. Spine department formed by twelve vertebrae
10. The channel in which the spinal cord is located
11. Brain located in the vertebral canal
12. Spinal cord function
13. Cage formed by twelve steam edges
Start of form
End of form

1. One of the skeletal departments of a free upper limb
2. Bone, forming a rolling compound with a spatula, allowing you to make various movements with hand
3. Upper limb
4. limbs with which a person performs labor operations
5. Limbs, the function of which is support and movement
6. One of the departments of the brush
7. One of the departments of the brush
8. The ability of this bone to rotate around the ulnash bone, allows you to perform such movements like key turning, screwdriver rotation
9. Steam bone, which is part of the belt of the upper limbs and resembles a shovel form
10. One of the departments of the brush
11. Skeleton Department of the Free Upper Limit
12. Steam bone, which is part of the belt of the upper extremities
13. Lower limb
14. Raewi + ...? \u003d forearm
15. Mobile connection that allows you to make various movements with hand
16. One of the skeletal departments of a free upper limb
17. Rayed + elbow \u003d?
Start of form
End of form

1. Bones of the skeleton of the foot.
2. Lower limbs man.
3. The largest massive bone of a skeleton of a person.
4. One of the bones is replied.
5. Bone of the leg.
6. Pelvic bones + crescents \u003d?
7. Bones are repulsed + plus + phalanges of fingers \u003d skeleton ...?
8. Small foot bones.
9. Bones of the skeleton of the foot.
10. Padelnik.
11. The bone of the skeleton of the foot.
12. One of the bones of the leg.
13. The pelvic bone + ...? + pelvic bone.
14. Belt of the lower extremities.
15. The bone, which is part of the skeleton of the free lower limb.
Start of form
End of form

1. Their three pairs.
2. Fixture for the introduction into the body of the enemy poison.
3. "Portrait of" insect.
4. The main organ of the insect senses.
5. With its insect feeds.
6. Wonderful apparatus, lifting an animal in the air.
7. Device for teaching eggs.
8. Apartment intestinal, digestive and germ.
9. They see ultraviolet rays and polarized light.
10. The capacity of powerful muscles leading to the movement of the wings and legs.
Start of form
End of form

1. The class of vertebrate animals, the main distinguishing features of which are eligible.
2. The detachment of placental mammals. The overwhelming majority of the detachment representatives are classic carnivorous animals that are mainly in vertebrates.
3. The most numerous detachment of mammals.
4. One of the most progressive detachments of placental mammals, including, including monkeys and a person.
5. The detachment of placental mammals is obliged to their name to their main distinctive sign - a trunk.
6. A group of mammals, combining seals and walrles.
7. The detachment of large ground mammals.
8. Animals of small size, with a short tail, or it is absent at all. Their teeth have some similarities with the teeth of rodents.
9. The name of the detachment is given for the presence of the animals of developed third and fourth fingers, the endings of which are covered with a thick horny hoof, like a case or shoe. The second and fifth fingers are underdeveloped, and the first is reduced.
10. The detachment of mammals relating to more archaic placental existing already in Eocene. They are well developed jaws and muscles for chewing. The main food is insects, waxes and worms.
11. The detachment of mammals fully adapted to life in water. They are the largest of the famous animals that ever having lived on Earth.
12. The detachment of placental mammals, the only one, whose representatives are capable of active flight. The science of chipterial is devoted to their research.
13. Subclass of primitive mammals connecting the features of mammals and reptiles.
Start of form
End of form

1. Marine mammals from chitty detachment, not related to dolphins, nor to sea pigs. Have the biggest dimensions among animals. Moreover, according to some reports, hippos are their closest relatives; They occurred OT. general ancestor Approximately 54 million years ago.
2. The biggest mammal on our planet.
3. One is the largest representatives Listonovyi.
4. Mammal, Feline Family. It is one of the largest land predators, yielding only white and brown bears by weight.
6. Animal family of non-parunopotable, domesticated. It is widely used by a person up to the present.
7. Predatory mammal Family kuni. It is found almost on all continents. The smallest squad is predatory.
8. Primates, from the Martish family, medium size with a strong torso and strong limbs.
9. Sobologol monkey.
10. Very beautiful mammal. The skin of the beast is a golden background, according to which the stains of black color are chaotically scattered.
11. These are small animals, externally similar to mice, but with a muzzle stretched in the form of a trunk. Eats four and a half times more than weighs itself. And he eats not only insects and their larvae, but also slugs, attacks even on mice.
12. Well-known in the appearance of the animal. The length of his body is about 20-30 cm, the tail is about 3 cm. The middle mass of about 700-800 g. The ears are relatively small. Needles are short (no more than 3 cm.). Head and belly covered with rude and usually dark-colored hair.
13. The largest modern deer.
14. Insectivorous small and medium sizes. Adapted to the underground, lifestyle. The torso is elongated, rounded, covered with thick, smooth, velvety fur.
15. This is a small rodent - thanks to the omnivities and the striking ability to adapt to the whole world.
16. Family of manfall. The branched horns are characterized, which are available only in males. They have rich symbolic importance and are in the myths of various cultures and peoples, personifying nobility, greatness, beauty, grace, speed.
17. The northernmost species of feline. An animal preferences with deaf dark forests, taiga, although it is found in a variety of plantations, including mountain forests; Sometimes it comes to the forest-steppe and foreman. It snaps perfectly on trees and rocks, well swims.
Start of form
End of form

1. Middle size deer. Rushing and exclusively herbivorous animal. Its food is the grass and foliage of trees. Sometimes it breaks and tree bark.
2. Marsh beaver.
3. Psure Mammal Family Pins.
4. Externally reminds donkey, but has a lot general signs with a horse.
5. Prescaring mammal of the pet family. Looks like a wolf, but significantly less than it in size, with a shorter tail and a pointed muzzle.
6. The mammal detachment is predatory. Very large and strong animal. Omnivorous, goes well and swims, runs quickly, can stand and pass short distances on the hind legs.
7. Excellent pet, excellent pet, who won sympathy not only children, but also adults.
8. Family of mannial, vegetative animals that feed on various parts of plants, including bark, leaves, herbs, kidneys, branches and a begower.
9. Powder Play Playground Mammal. An important hunting animal beast.
10. Mammal from a piece of manflock, is the highest ground animal planet.
11. Mammals, representatives of Rodent detachment. Herbivorous, settles in Norah, has a warm fur.
12. Beast a little more cones. It has an elongated body with a fluffy long tail, the ears are long, the color is dark brown with a white belly, sometimes gray. A characteristic feature is the ability to store nuts for the winter. Some types of nuts are buried in the ground, others hide them in the wrappers of trees.
13. Muscic rat. Semi-water rodent.
14. Four commercial animal, which is sometimes called polar fox.
15. Or Ishack.
Start of form
End of form

1. Almost all representatives of this family are grass. Stem Solmin. Small flowers are collected one or more in spikelets forming complex inflorescences. The fruit is a grain. Seed with an abundant endosperm and adjacent to him with a small embryo, occupying one end of the seed.
2. Representatives of this family are distributed almost all over the globe. One of the most important in the economic relationship of the groups of the plant kingdom. Many family representatives are widely used as medicinal, technical, decorative plants, are appreciated as honey. They are characterized by symbiosis with nitrogen-fixing nodule bacteria, which improves the soil enriching it with nitrogen.
3. Up to 1500 species common in the northern hemisphere. Some species are cultivated as food and decorative plants.
4. Completed both in the tropics and subtropics and in areas moderate climate. The family has a lot of decorative species (irises, gladiolus, saffron, etc.), as well as a number of medicinal, food, ethereal, and dyeing plants. Perennials with underground rhizomes or clubnellukov. Fruits - a box with numerous seeds.
5. Shrubs with simple regular leaves. A cup of 5 cups that have grown into the tube growing towards the wound. Stamens 5. Fruits - juicy multifamous berries. Seeds with endosperm. A number of species refers to the number of food (berry) plants; Some are bred as decorative.
6. One of the taxonomic units.
Start of form
End of form

1. Root, developing from stem or sheet.
2. Axial vegetative organ plant with unlimited top growth, positive geotropism, having a radial structure and never bearing leaves.
3. Branch of the main, lateral or apparent root.
4. Root system with well-pronounced main root.
5. A modified thickened side or gifted root that performs the function of the supply of nutrients.
6. The root zone where the cell size increases and their specialization begins.
7. Zone, where the increasing cone, represented by the upheld educational fabric, provides a root growth in length due to the continuous division of cells.
8. The root zone, located above the suction zone, where water and mineral salts are moving along the vessels, and carbohydrates are moved along the sieve tubes.
9. Root, developing from the embryonic root.
10. The root system presented mainly by the apparent roots, which does not stand out by the main root.
11. Moving as the zone is growing, where the cell specialization occurs in various tissues and suction of water from the soil using root hairs.
12. Protective, constantly updating cells education at the top of the growing root.
13. A modified thickened main root carrying a shortened escape at the base and performing the function of the supply of nutrients.
Start of form
End of form

1. Stem with leaves and kidneys.
2. Perennial wood plants giving powerful side shoots at the surface of the soil. The main trunk is noticeable only in young plants.
3. Complex Sciences About Plants: Classification, historical development, morphology ( external structure), anatomy ( internal structure), physiology, ecology, etc.
4. Dry multifermeal fruit, whose seeds are located on sash (peas, beans)
5. One of the main vegetative leafy plant organs serving to attach to the substrate, the absorption of water and nutrients from it.
6. Fruit having a well-developed pulp with a large amount of juice containing various acids, sugar (cranberries, grapes, cherry).
7. Sukhai multifaceted fruit of two sash, separated by a film partition; Seeds are located on the partition (cabbage, turnip, radishes).
8. Juicy multi-free fruits (tomato, grapes, currants).
9. Annual and perennial plants with soft or juicy ground stems that die with adverse seasonal climate change.
10. The organ of reproduction of covered brine (flowering) plants.
11. Dry single-chain fruit with relatively thin leathery spindlers, easily separated from the seed (sunflower, dandelion).
12. Knowledge System seasonal events Nature, the timing of their occurrence and the reasons defining these terms.
13. Dry single-in-law fruit with a subtle octoplate, tightly pressed to seed and growing with it only at the base (rye, wheat, barley).
14. Research, educational and cultural and educational gardens, in which collections of living plants are collected and based on their diversity and wealth. vegetable world Earth.
15. Fruit without succulent pulp, and contains one, or a lot of seeds (acorn, walnut, bob at beans).
16. The low-spirited perennial plants with wood, highly branched shoots, usually do not have a clearly pronounced main trunk (lingonberry, blueberry).
17. Juicy, single-hearted fetus with a solid bone (plum, cherry).
18. Perennial plants with a decisive main trunk that remains throughout life, and a crown (spruce, birch).
19. The organ of reproduction and resettlement of plants, developing from a seed and launching in the flowering plants, in which it is enclosed in a fruit, or lies, openly on the scales of the bumps from the vicered.
20. The organ that develops from the vegetation of the flower and the concluding seeds whose function is the formation, protection and distribution of seeds.
Start of form
End of form

1. Annual herbate plant Leading grain culture in many countries of the world.
2. The thermo-loving, light-affilome and moisture-loving plant. Used in the food industry for the manufacture of flour, oil, margarine, confectionery, in the production of artificial fibers, plastics, glue, varnishes, paints, soap, as well as for feed in the form of green mass and hay for animal s / cock
3. Perennial tuberous vegetable culture.
4. Drought-resistant herbaceous plant. Seeds have a fatty food oil, allyl oil, which is necessary in medicine.
5. Annual thermal-loving plant grown to obtain oil from seed. Fiber is suitable for producing burlap, tarpaulin, twine.
6. Two-year vegetable and aft culture. Casuals and leaves contain carbohydrates, proteins and mineral salts, vitamins C and group B, etc.
7. The light-lubricant, moisture-loving, thermo-loving plant. Seeds contain from 37 to 57% oil, which is directly in food, industry - soap, paintwork production.
Crossword with questions and answers for schoolchildren 5 - 8th grade. "Young entomologist".
Makeeva Nelya Nikolaevna, teacher of biology and chemistry, MBOU "Perkhlajskaya Oosh", Ruzaevsky R-, p. Plug.Description: This Crossword Budyud is useful to class managers, additional education teachers. It can be used in individual or group work in lessons, extracurricular work.
Purpose: Development of the interest of schoolchildren to the insectivoid.
Tasks:
- deepen and expand the knowledge of schoolchildren about insects of our planet;
- teach to solve crosswords;
- develop inquisitiveness in children and creative activity.
Crossword on the topic: "Young entomologist"

1. What insects eat steppe viper?
3. Which OSA takes care of his children?
4. Insect that lives together?
6. The detachment of insects without eyes and without a mustache?
7. Which insects are the main wealth?
10. What is the bee makes the hives from El?
11. Klop ...
12. Amquesncalp moth houses.
13. Insect Living together.
16. Insect with screking eyes.
18. Insect beetle.
19. Apple ...
21. Beetle, which hides in the wood?

Vertical Questions:
2. Who takes a strange pose in the heat?
5. Become a migranet from America?
8. Deserted ...
9. A resident of the steppes and deserts?
14. Holy Beetle.
15. Osa ...
17. Large mothers?
20. Double squad?

Answers to Crossword:
Horizontally:1. Saranscha
3. Evemen.
4. Multi-stroke
6. Best-making
7. Ants
10. Ilnitsa
11. Goeblak
12. Galla
13. Multi-stroke
16. Bogomol
18. Skakun.
19. Mol.
21. Usach
Vertically:
2. Dragonfly
5. Colorado
8. Fall
9. Chernotelka
14. Scarab
15. Ammofilla
17. TLL
20. Komar






